What vital processes take place in the cell nucleus. The science that studies the structure and functioning of cells
Option 9. Unified State Exam 2014,
When completing tasks in this part, in the answer form Ml, under the number of the task you are performing (A1-A36), put an “x” in the box whose number corresponds to the number of the answer you have chosen.
A1. The study of the structure of the smallest cell organelles and large molecules became possible after the invention
1) hand-held magnifier
2) electron microscope
3) tripod magnifier
4) light microscope
A2. The similarity in the structure and functioning of the cells of all organisms indicates their
1) kinship 3) evolutionary process
2) diversity 4) fitness
A3. Chemical basis chromosomes are made up of a molecule
1) ribonucleic acid
3) deoxyribonucleic acid
4) polysaccharide
A4. The formation of two cells with a diploid set of chromosomes from one mother cell is characteristic of the process
1) mitosis 3) egg maturation
2) crossing over 4) meiosis
A5. They function only in the cell of another organism, using its amino acids, enzymes and energy for synthesis nucleic acids and proteins
1) bacteria 3) lichens
2) application of organic fertilizers
3) destruction of weeds with herbicides
A26. Natural areas, where all types of economic activity humans in order to restore the number of rare species of plants and animals, represent
1) agrocenoses
2) reserves
3) botanical gardens
4) shelterbelts
A27. Breakdown of lipids to glycerol and fatty acids with the participation of enzymes in the cell occurs in
1) mitochondria 3) lysosomes
2) ribosomes 4) chloroplasts
A28. What number of nucleotides in a gene section encodes the primary structure of a protein consisting of 300 amino acids?
A29. During mitotic division at the end of anaphase in a human cell, the number of DNA molecules is equal to
A30. The diploid set of bread wheat has 42 chromosomes. The new variety obtained on its basis has 84 chromosomes due to
1) changes in reaction norm
2) cytoplasmic mutation
3) chromosomal rearrangements
4) nondisjunction of chromosomes in meiosis
A31. Disruption of the process of spindle formation in meiosis causes the appearance of
1) heterosis 3) modifications
2) polyploids 4) gene mutations
A32. In bamboo, a representative of the class Monocots
1) reticulate venation of leaves
2) simple and compound leaves with stipules
3) the seed contains two cotyledons
4) fibrous root system
A33. In humans, blood enters the right atrium through the superior vena cava from the vessels of the brain and upper extremities
1) arterial 3) mixed
2) venous 4) oxygenated
A34. Internal inhibition in humans is accompanied by
1) extinction of the conditioned reflex
2) reflexive cessation of breathing
3) weakening of unconditioned reflexes
4) formation of an unconditioned reflex
A35. Macroevolution, unlike microevolution, leads to
1) increased competition of existing species
2) the formation of new species of plants and animals
3) the formation of large taxonomic groups
4) weakening of the effect driving forces evolution
A36. Are the following statements about ecosystems and their inherent patterns true?
A. The food chain starting with plants is called the decomposition chain or detritus chain.
B. Another type of food chain starts from plant and animal remains, animal excrement, it is called the grazing or grazing chain.
1) only A is true 3) both judgments are true
2) only B is true 4) both judgments are incorrect
PART 2
B1. What vital processes occur in the cell nucleus?
1) formation of the spindle
2) formation of lysosomes
3) doubling of DNA molecules
4) synthesis of mRNA molecules
5) formation of mitochondria
6) formation of ribosomal subunits
AT 2. Signs of the structure and functions of the human pancreas:
1) performs a barrier role
2) produces bile
4) has exocrine and intrasecretory parts
5) has ducts that open into the duodenum
6) produces digestive juice that breaks down proteins, fats, carbohydrates
AT 3. Which of the following examples are classified as idioadaptations?
1) the presence of a waxy coating on cranberry leaves
2) bright juicy pulp of blueberries
3) the presence of mammary glands in mammals
4) the appearance of a complete septum in the heart in birds
5) flattened body shape in stingrays
6) double fertilization in angiosperms
B4. Establish a correspondence between the trait and the plant division for which it is characteristic.
SIGN PLANT DEPARTMENT
practically never occur
B) life forms: trees, shrubs and grasses
D) fruits with seeds
D) most have needle-shaped leaves (needles)
SUBSTANCE OF THE BIOSPHERE
2) biogenic
AT 5. Establish a correspondence between the function of a neuron and its type.
A) converts irritations into nerve impulses
B) transmits nerve impulses from the senses and internal organs to the brain
B) transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another in the brain
D) transmits nerve impulses to muscles, glands and other executive organs
NEURON TYPE
1) sensitive
2) insertion
3) motor
AT 6. Establish a correspondence between the trait and the form of life for which it is characteristic.
LIFE FORM
1) non-cellular (viruses)
2) cellular (bacteria)
A) the presence of ribosomes
B) absence plasma membrane
B) does not have its own metabolism
D) most are heterotrophs
D) reproduction only in host cells
E) reproduction by cell division
AT 7. Establish a correspondence between a natural object and the substance of the biosphere to which it belongs.
A) granite
B) basalt
B) coal
SUBSTANCE OF THE BIOSPHERE
2) biogenic
AT 8. Establish the sequence of emergence of groups of invertebrate animals in the process of historical development.
1) flatworms
2) unicellular animals
3) coelenterates
4) annelids
5) colonial unicellular organisms
6) arthropods
To answer the tasks in this part (C1-C6), use answer form No. 2. First write down the task number (C1, etc.), then the answer to it. Give a short free answer to task C1, and give a full, detailed answer to tasks C2-C6.
C1. What is the nature of most enzymes, and why do they lose their activity as radiation levels increase?
C2. What process is shown in the picture? What underlies this process and how does the composition of the blood change as a result? Explain your answer.
 C3. What is the impact of physical inactivity (low physical activity) on the human body?
C3. What is the impact of physical inactivity (low physical activity) on the human body?
C4. Give at least three progressive biological characteristics of a person that he acquired in
process of long evolution.
C5. TRNAs with anticodons: UUA, GGC, TsShch, AUU, TsGU participated in the biosynthesis of the polypeptide. Determine the nucleotide sequence of the section of each chain of the DNA molecule that carries information about the polypeptide being synthesized, and the number of nucleotides containing adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C) in a double-stranded DNA molecule. Explain your answer.
C6. Diheterozygous corn plants with brown colored (A) and smooth (B) seeds were pollinated with pollen from corn with white colored seeds and their wrinkled shape. The offspring produced 4,000 seeds by similar to the parents (2002 brown smooth seeds and 1998 white wrinkled seeds), as well as 152 brown wrinkled and 149 white smooth corn seeds. Dominant and recessive genes for these traits are linked in pairs. Make a diagram for solving the problem. Determine the genotypes of parental corn plants and offspring, give reasons for the appearance of two groups of individuals with characteristics different from their parents.
Response elements:
1) most enzymes are proteins
2) under the influence of radiation, denaturation occurs, the structure of the protein-enzyme changes
Response elements:
1) the figure shows gas exchange in the lungs (between the pulmonary vesicle and the blood capillary);
2) gas exchange is based on diffusion - the penetration of gases from a place with high pressure to a place with
less pressure;
3) as a result of gas exchange, venous blood (A) turns into arterial blood (B).
Response elements:
1) physical inactivity causes stagnation venous blood V lower limbs, which can lead to weakening
valve function and vasodilation;
2) metabolism decreases, which leads to an increase in adipose tissue and excess body weight;
3) muscles weaken, the load on the heart increases and the body’s endurance decreases
Response elements:
1)enlargement of the brain and brain section skulls;
2) upright posture and corresponding changes in the skeleton;
3) liberation and development of the hand, opposition thumb everyone else
2) a section of one DNA strand is TTAGGCCCHATTCGT, and the composition of the second DNA strand is AATCCGGCGTAASCHA;
3) number of nucleotides: A - 7, T - 7, G - 8, C - 8.
The problem solution scheme includes:
1) genotypes of the parents: AaBb and aabb;
2) progeny genotypes AaBb (brown smooth) and aabb (white wrinkled) - 4000 seeds
(2002+1998); Aabb (brown wrinkled) and aaBb (white smooth) - 152 and 149 seeds;
3) the appearance of two groups of individuals with characteristics distinctive from their parents is associated with the conjugation and crossing of chromosomes, the formation of four types of gametes in the parent heterozygous organism:
AB, ab, Ab, aB.
At the dawn of the development of life on Earth, everything cell forms were represented by bacteria. They absorbed organic substances dissolved in the primordial ocean through the surface of the body.
Over time, some bacteria have adapted to produce organic substances from inorganic ones. To do this, they used the energy of sunlight. The first ecological system arose in which these organisms were producers. As a result, oxygen released by these organisms appeared in the Earth's atmosphere. With its help, you can get much more energy from the same food, and use the additional energy to complicate the structure of the body: dividing the body into parts.
One of important achievements life - separation of nucleus and cytoplasm. The nucleus contains hereditary information. A special membrane around the core made it possible to protect against accidental damage. As needed, the cytoplasm receives commands from the nucleus that direct the life and development of the cell.
Organisms in which the nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm have formed the nuclear superkingdom (these include plants, fungi, and animals).
Thus, the cell - the basis of the organization of plants and animals - arose and developed in the course of biological evolution.
Even with the naked eye, or even better under a magnifying glass, you can see that the pulp of a ripe watermelon consists of very small grains, or grains. These are cells - the smallest “building blocks” that make up the bodies of all living organisms, including plants.
The life of a plant is carried out by the combined activity of its cells, creating a single whole. With multicellularity of plant parts, there is a physiological differentiation of their functions, specialization of various cells depending on their location in the plant body.
A plant cell differs from an animal cell in that it has a dense membrane that covers the internal contents on all sides. The cell is not flat (as it is usually depicted), it most likely looks like a very small bubble filled with mucous contents.
Structure and functions of a plant cell
Let's consider a cell as a structural and functional unit of an organism. The outside of the cell is covered with a dense cell wall, in which there are thinner sections called pores. Beneath it there is a very thin film - a membrane covering the contents of the cell - the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm there are cavities - vacuoles filled with cell sap. In the center of the cell or near the cell wall there is a dense body - a nucleus with a nucleolus. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope. Small bodies called plastids are distributed throughout the cytoplasm.
Structure of a plant cell
Structure and functions of plant cell organelles
| Organoid | Drawing | Description | Function | Peculiarities |
Cell wall or plasma membrane | Colourless, transparent and very durable | Passes substances into and out of the cell. | Cell membrane semi-permeable |
|
Cytoplasm | Thick viscous substance | All other parts of the cell are located in it | Is in constant motion |
|
Nucleus (important part of the cell) | Round or oval | Ensures the transfer of hereditary properties to daughter cells during division | Central part of the cell |
|
Spherical or irregular in shape | Takes part in protein synthesis | |||
 | A reservoir separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane. Contains cell sap | Spare nutrients and waste products that the cell does not need accumulate. | As the cell grows, small vacuoles merge into one large (central) vacuole |
|
Plastids | Chloroplasts | They use the light energy of the sun and create organic from inorganic | The shape of discs delimited from the cytoplasm by a double membrane |
|
Chromoplasts | Formed as a result of the accumulation of carotenoids | Yellow, orange or brown |
||
 | Leukoplasts | Colorless plastids | ||
Nuclear envelope | Consists of two membranes (outer and inner) with pores | Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm | Allows exchange between the nucleus and cytoplasm |
The living part of a cell is a membrane-bound, ordered, structured system of biopolymers and internal membrane structures involved in a set of metabolic and energy processes that maintain and reproduce the entire system as a whole.
An important feature is that the cell does not have open membranes with free ends. Cell membranes always limit cavities or areas, closing them on all sides.
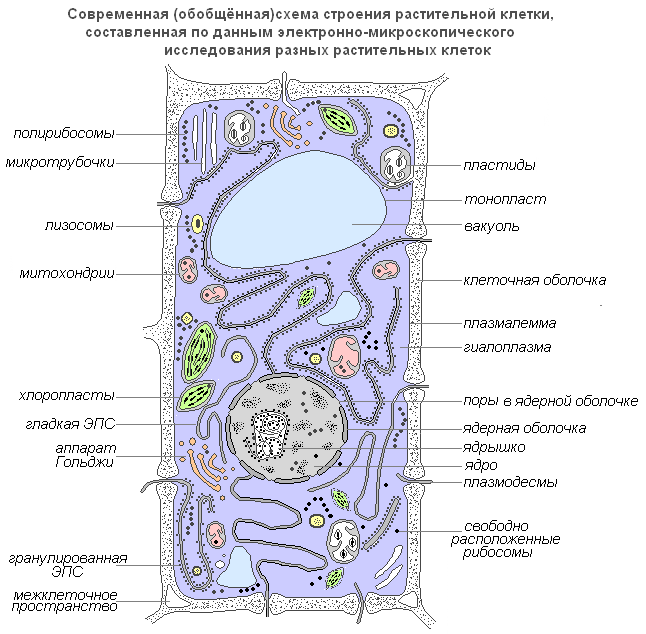
Modern generalized diagram of a plant cell
Plasmalemma(outer cell membrane) is an ultramicroscopic film 7.5 nm thick, consisting of proteins, phospholipids and water. This is a very elastic film that is well wetted by water and quickly restores integrity after damage. It has a universal structure, i.e. typical for all biological membranes. In plant cells, outside the cell membrane there is a strong cell wall that creates external support and maintains the shape of the cell. It consists of fiber (cellulose), a water-insoluble polysaccharide.
Plasmodesmata plant cells, are submicroscopic tubules that penetrate the membranes and are lined with a plasma membrane, which thus passes from one cell to another without interruption. With their help, intercellular circulation of solutions containing organic nutrients occurs. They also transmit biopotentials and other information.
Porami called openings in the secondary membrane, where the cells are separated only by the primary membrane and the median lamina. The areas of the primary membrane and the middle plate separating the adjacent pores of adjacent cells are called the pore membrane or the closing film of the pore. The closing film of the pore is pierced by plasmodesmal tubules, but a through hole is usually not formed in the pores. Pores facilitate the transport of water and solutes from cell to cell. Pores form in the walls of neighboring cells, usually one opposite the other.
Cell membrane has a well-defined, relatively thick shell of a polysaccharide nature. The plant cell membrane is a product of the activity of the cytoplasm. The Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum take an active part in its formation.

Structure of the cell membrane
The basis of the cytoplasm is its matrix, or hyaloplasm, a complex colorless, optically transparent colloidal system capable of reversible transitions from sol to gel. The most important role of hyaloplasm is to unite all cellular structures V unified system and ensuring interaction between them in the processes of cellular metabolism.
Hyaloplasma(or cytoplasmic matrix) is internal environment cells. It consists of water and various biopolymers (proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, lipids), of which the main part consists of proteins of varying chemical and functional specificity. The hyaloplasm also contains amino acids, monosaccharides, nucleotides and other low molecular weight substances.
Biopolymers form a colloidal medium with water, which, depending on conditions, can be dense (in the form of a gel) or more liquid (in the form of a sol), both throughout the cytoplasm and in its individual sections. In the hyaloplasm, various organelles and inclusions are localized and interact with each other and the hyaloplasm environment. Moreover, their location is most often specific to certain types cells. Through the bilipid membrane, the hyaloplasm interacts with the extracellular environment. Therefore, hyaloplasm is a dynamic medium and plays important role in the functioning of individual organelles and the life of cells as a whole.
Cytoplasmic formations - organelles
Organelles (organelles) - structural components cytoplasm. They have a certain shape and size and are obligatory cytoplasmic structures of the cell. If they are absent or damaged, the cell usually loses its ability to continue to exist. Many of the organelles are capable of division and self-reproduction. Their sizes are so small that they can only be seen with an electron microscope.
Core
The nucleus is the most prominent and usually the largest organelle of the cell. It was first explored in detail by Robert Brown in 1831. The nucleus provides the most important metabolic and genetic functions of the cell. It is quite variable in shape: it can be spherical, oval, lobed, or lens-shaped.
The nucleus plays a significant role in the life of the cell. A cell from which the nucleus has been removed no longer secretes a membrane and stops growing and synthesizing substances. The products of decay and destruction intensify in it, as a result of which it quickly dies. The formation of a new nucleus from the cytoplasm does not occur. New nuclei are formed only by dividing or crushing the old one.
The internal contents of the nucleus are karyolymph (nuclear juice), which fills the space between the structures of the nucleus. It contains one or more nucleoli, as well as a significant number of DNA molecules connected to specific proteins - histones.

Core structure
Nucleolus
The nucleolus, like the cytoplasm, contains predominantly RNA and specific proteins. Its most important function is that it forms ribosomes, which carry out the synthesis of proteins in the cell.
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that is universally distributed in all types of eukaryotic cells. It is a multi-tiered system of flat membrane sacs, which thicken along the periphery and form vesicular processes. It is most often located near the nucleus.

Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus necessarily includes a system of small vesicles (vesicles), which are detached from thickened cisterns (discs) and are located along the periphery of this structure. These vesicles play the role of an intracellular transport system for specific sector granules and can serve as a source of cellular lysosomes.
The functions of the Golgi apparatus also consist of the accumulation, separation and release outside the cell with the help of vesicles of intracellular synthesis products, breakdown products, and toxic substances. Products of the synthetic activity of the cell, as well as various substances, entering the cell from environment through the channels of the endoplasmic reticulum, are transported to the Golgi apparatus, accumulate in this organelle, and then in the form of droplets or grains enter the cytoplasm and are either used by the cell itself or excreted outside. IN plant cells The Golgi apparatus contains enzymes for the synthesis of polysaccharides and the polysaccharide material itself, which is used to build cell membrane. It is believed that it is involved in the formation of vacuoles. The Golgi apparatus was named after the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi, who first discovered it in 1897.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are small vesicles bounded by a membrane whose main function is to carry out intracellular digestion. The use of the lysosomal apparatus occurs during the germination of a plant seed (hydrolysis of reserve nutrients).

Structure of a lysosome
Microtubules
Microtubules are membranous, supramolecular structures consisting of protein globules arranged in spiral or straight rows. Microtubules perform a predominantly mechanical (motor) function, ensuring the mobility and contractility of cell organelles. Located in the cytoplasm, they give the cell a certain shape and ensure the stability of the spatial arrangement of organelles. Microtubules facilitate the movement of organelles to places determined by the physiological needs of the cell. Significant amount These structures are located in the plasmalemma, near the cell membrane, where they participate in the formation and orientation of cellulose microfibrils of plant cell membranes.

Microtubule structure
Vacuole
The vacuole is the most important component of plant cells. It is a kind of cavity (reservoir) in the mass of the cytoplasm, filled aqueous solution mineral salts, amino acids, organic acids, pigments, carbohydrates and separated from the cytoplasm by a vacuolar membrane - the tonoplast.
Cytoplasm fills the entire internal cavity only in the youngest plant cells. As the cell grows, the spatial arrangement of the initially continuous mass of cytoplasm changes significantly: small vacuoles filled with cell sap appear, and the entire mass becomes spongy. With further cell growth, individual vacuoles merge, pushing the layers of cytoplasm to the periphery, as a result of which the formed cell usually contains one large vacuole, and the cytoplasm with all organelles is located near the membrane.
Water-soluble organic and mineral compounds of vacuoles determine the corresponding osmotic properties of living cells. This solution of a certain concentration is a kind of osmotic pump for controlled penetration into the cell and release of water, ions and metabolite molecules from it.
In combination with the cytoplasm layer and its membranes, characterized by semi-permeable properties, the vacuole forms an effective osmotic system. Osmotically determined are such indicators of living plant cells as osmotic potential, suction force and turgor pressure.

Structure of the vacuole
Plastids
Plastids are the largest (after the nucleus) cytoplasmic organelles inherent only to cells plant organisms. They are not found only in mushrooms. Plastids play an important role in metabolism. They are separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane shell, and some types have a well-developed and ordered system of internal membranes. All plastids are of the same origin.
Chloroplasts- the most common and most functionally important plastids of photoautotrophic organisms that carry out photosynthetic processes, ultimately leading to the formation of organic substances and the release of free oxygen. The chloroplasts of higher plants have a complex internal structure.

Chloroplast structure
The sizes of chloroplasts in different plants are not the same, but on average their diameter is 4-6 microns. Chloroplasts are able to move under the influence of the movement of the cytoplasm. In addition, under the influence of lighting, active movement of amoeboid-type chloroplasts towards the light source is observed.
Chlorophyll is the main substance of chloroplasts. Thanks to chlorophyll green plants capable of using light energy.
Leukoplasts(colorless plastids) are clearly defined cytoplasmic bodies. Their sizes are somewhat smaller than the size of chloroplasts. Their shape is also more uniform, approaching spherical.

Leukoplast structure
Found in epidermal cells, tubers, and rhizomes. When illuminated, they very quickly turn into chloroplasts with a corresponding change in the internal structure. Leucoplasts contain enzymes with the help of which starch is synthesized from excess glucose formed during photosynthesis, the bulk of which is deposited in storage tissues or organs (tubers, rhizomes, seeds) in the form of starch grains. In some plants, fats are deposited in leucoplasts. The reserve function of leukoplasts occasionally manifests itself in the formation of reserve proteins in the form of crystals or amorphous inclusions.
Chromoplasts in most cases they are derivatives of chloroplasts, occasionally - leucoplasts.

Chromoplast structure
The ripening of rose hips, peppers, and tomatoes is accompanied by the transformation of chloro- or leucoplasts of the pulp cells into caratinoid plasts. The latter contain predominantly yellow plastid pigments - carotenoids, which, when ripe, are intensively synthesized in them, forming colored lipid droplets, solid globules or crystals. In this case, chlorophyll is destroyed.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles characteristic of most plant cells. They have a variable shape of sticks, grains, and threads. Discovered in 1894 by R. Altman using a light microscope, and the internal structure was studied later using an electron microscope.

The structure of mitochondria
Mitochondria have a double-membrane structure. The outer membrane is smooth, the inner one forms various shapes outgrowths are tubes in plant cells. The space inside the mitochondrion is filled with semi-liquid content (matrix), which includes enzymes, proteins, lipids, calcium and magnesium salts, vitamins, as well as RNA, DNA and ribosomes. The enzymatic complex of mitochondria accelerates the complex and interconnected mechanism of biochemical reactions that result in the formation of ATP. In these organelles, cells are provided with energy - the energy of chemical bonds of nutrients is converted into high-energy bonds of ATP in the process of cellular respiration. It is in the mitochondria that it occurs enzymatic digestion carbohydrates, fatty acids, amino acids with the release of energy and its subsequent conversion into ATP energy. The accumulated energy is spent on growth processes, on new syntheses, etc. Mitochondria multiply by division and live for about 10 days, after which they are destroyed.
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of channels, tubes, vesicles, and cisterns located inside the cytoplasm. Discovered in 1945 by the English scientist K. Porter, it is a system of membranes with an ultramicroscopic structure.

Structure of the endoplasmic reticulum
The entire network is united into a single whole with the outer cell membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are smooth and rough ER, which carries ribosomes. On the membranes of the smooth ER there are enzyme systems involved in fat and carbohydrate metabolism. This type of membrane predominates in seed cells rich in storage substances (proteins, carbohydrates, oils); ribosomes are attached to the granular ER membrane, and during the synthesis of a protein molecule, the polypeptide chain with ribosomes is immersed in the ER channel. The functions of the endoplasmic reticulum are very diverse: transport of substances both within the cell and between neighboring cells; division of a cell into separate sections in which various physiological processes and chemical reactions simultaneously take place.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are non-membrane cellular organelles. Each ribosome consists of two particles that are not identical in size and can be divided into two fragments, which continue to retain the ability to synthesize protein after combining into a whole ribosome.

Ribosome structure
Ribosomes are synthesized in the nucleus, then leave it, moving into the cytoplasm, where they attach to outer surface membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum or are located freely. Depending on the type of protein being synthesized, ribosomes can function alone or be combined into complexes - polyribosomes.
Test on the topic: «
1. The main postulates of the “cellular theory” were formulated in 1838-1839:
1. A. Leeuwenhoek, R. Brown
2. T. Schwann, M. Schleiden
3. R. Brown, M. Schleiden
4.T. Schwann, R. Virchow.
2. Photosynthesis occurs:
1. in chloroplasts 2. in vacuoles
3. in leukoplasts 4. in the cytoplasm
3. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates are stored in reserve:
1. in ribosomes 2. in the Golgi complex
3. in mitochondria 4. in cytoplasm
4. What proportion (%) in a cell is on average macroelements?
1. 80% 2. 20 % 3. 40% 4. 98%
5. Cells do not synthesize organic substances, but use ready-made ones
1. autotrophs 2. heterotrophs
3. prokaryotes 4. eukaryotes
6. One of the functions of the cell center
1. Formation of the spindle
2. Formation of the nuclear envelope
3. Control of protein biosynthesis
4. Movement of substances in the cell
7. Occurs in lysosomes
1. Protein synthesis
2. Photosynthesis
3. Breakdown of organic substances
4. Chromosome conjugation
8.
| organoids | characteristics |
| 1Plasma membrane | |
| B. Protein synthesis. |
|
| 3Mitochondria | B. Photosynthesis. |
| 4Plastids | |
| 5Ribosomes | |
| E. Non-membrane. |
|
| 7Cell center | G. Synthesis of fats and carbohydrates. |
| 8Golgi complex | 3. Contains DNA. |
| I. Single membrane |
|
| 10Lysosomes | M. Double membrane. A. Only plants have it. P. Only plants have it. |
9. Membranes and channels of the granular endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carry out the synthesis and transport of:
1. proteins 2. lipids
3. carbohydrates 4. nucleic acids.
10. In the tanks and vesicles of the Golgi apparatus:
1. secretion of proteins
2. protein synthesis, secretion of carbohydrates and lipids
3. synthesis of carbohydrates and lipids, secretion of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
4. synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates, secretion of lipids and carbohydrates.
11.The cell center is present in cells:
1. all organisms 2. only animals
3. only plants 4. all animals and lower plants.
Second part
B-1 Which cell structures undergo the greatest changes during the process? mitosis?
1) nucleus 4) lysosomes
2) cytoplasm 5) cell center
3) ribosomes 6) chromosomes
AT 2. What functions does the Golgi complex perform in a cell?
1) protein synthesis
2) forms lysosomes
3) ensures the assembly of ribosomes
4) participates in the oxidation of substances
5) ensures the packaging of substances into secretory vesicles
6) participates in the release of substances outside the cell
B-3 Establish a correspondence between the metabolic feature and the group of organisms for which it is characteristic.
FEATURE ORGANISMS
a) release of oxygen into the atmosphere 1) autotrophs
b) use of food energy for ATP synthesis 2) heterotrophs
c) use of ready-made organic substances
d) synthesis of organic substances from inorganic ones
e) use carbon dioxide for food
AT 4. Establish a correspondence between the process occurring in the cell and the organelle for which it is characteristic.
ORGANOID PROCESS
A) reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose 1) mitochondria
B) ATP synthesis during respiration 2) chloroplast
B) primary synthesis of organic substances
D) conversion of light energy into chemical energy
D) the breakdown of organic substances into carbon dioxide and water.
Test on the topic: « Cellular structure organisms"
1. Cell membranes consist of:
1. plasmalemma (cytoplasmic membrane)
2. plasmalemmas in animals and cell walls in plants
3. cell walls
4. plasmalemmas in animals, plasmalemmas and cell walls in plants.
2. The functions of “power stations” are performed in the cage:
1. ribosomes
2. mitochondria
3. cytoplasm
4. vacuoles
3.Organoid involved in cell division:
1. ribosomes
2. plastids
3. Mitochondria
4.cell center
4. Cells that synthesize organic substances from inorganic ones
1. autotrophs
2. heterotrophs
3. prokaryotes
4. eukaryotes
5. Science that studies the structure and functioning of cells
1.Biology 2.Cytology
3.Histology 4. Physiology
6.Non-membrane cell organelle
1. Cell center 2. Lysosome
3. Mitochondria 4. Vacuole
7.
Distribute the characteristics according to the cell organelles (put letters
corresponding to the characteristics of the organoid, opposite the name of the organoid).
| organoids | characteristics |
| Plasma membrane | A. Transport of substances throughout the cell. |
| B. Protein synthesis. |
|
| Mitochondria | B. Photosynthesis. |
| Plastids | D. Movement of organelles throughout the cell. |
| Ribosomes | D. Storage of hereditary information. |
| E. Non-membrane. |
|
| Cell center | G. Synthesis of fats and carbohydrates. |
| Golgi complex | 3. Contains DNA. |
| I. Single membrane |
|
| Lysosomes | K. Providing the cell with energy. L. Self-digestion of cells and intracellular digestion. M. Double membrane. H. Cell connection with external environment. A. Only plants have it. P. Only plants have it. |
8. The main storage carbohydrate in animal cells:
1. starch 2. glucose 3. glycogen 4. fat
9. Membranes and channels of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carry out the synthesis and transport of:
1 proteins and carbohydrates 2 lipids 3 fats and carbohydrates 4 nucleic acids
10.Lysosomes are formed on:
1. channels of smooth EPS
2. channels of rough EPS
3. tanks of the Golgi apparatus
4. inner surface of the plasmalemma.
11. Microtubules of the cell center participate in the formation of:
1. only the cytoskeleton of the cell
2. spindles
3. flagella and cilia
4. cell cytoskeleton, flagella and cilia.
Second part
B-1. The basic principles of cell theory allow us to conclude that
1)biogenic migration of atoms
2) relatedness of organisms
3) the origin of plants and animals from a common ancestor
4) the appearance of life about 4.5 billion years ago
5) similar structure of cells of all organisms
6) the relationship between living and inanimate nature
Q-2 What vital processes occur in the cell nucleus?
1) formation of the spindle
2) formation of lysosomes
3) doubling of DNA molecules
4) RNA synthesis
5) formation of mitochondria
6) formation of ribosomes
B-3 Establish a correspondence between the structure, function of cell organelles and their type.
STRUCTURE, FUNCTIONS ORGANOIDS
B) provides oxygen formation
D) ensures the oxidation of organic substances
Q-4 What functions does the plasma membrane perform in a cell?
1) gives the cell a rigid shape.
2) delimits the cytoplasm from the environment
3) synthesizes RNA
4) promotes the entry of ions into the cell
5) ensures the movement of substances in the cell
6) participates in phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
ANSWERS
IN 11-2, 2-1, 3-2, 4-4, 5-2, 6-1, 7-3, 8-1n, 2d, 3k, 4mo, 5b, 6zh, 7e, 8a, 9gp, 10l; 9-1,10-3,11-4
V-1 156; V-2 256; B-3 12211; B-4 21221.
AT 21-4, 2-2, 3-4, 4-1,5-2, 6-1, 7-1n, 2d, 3k, 4mo, 5b, 6zh, 7e, 8a, 9gp, 10l; 8-3, 9-3, 10-3,11-2
V-1 235; V-2 346; V-3 21212; B-4 246.
Test on the topic: «
1. The main postulates of the “cellular theory” were formulated in 1838-1839:
1. A. Leeuwenhoek, R. Brown
2. T. Schwann, M. Schleiden
3. R. Brown, M. Schleiden
4.T. Schwann, R. Virchow.
2. Photosynthesis occurs:
1 . in chloroplasts 2. in vacuoles
3 . in leukoplasts 4. in the cytoplasm
3. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates are stored in reserve:
1 . in ribosomes 2. in the Golgi complex
3 . in mitochondria 4. in the cytoplasm
4. What proportion (%) in a cell is on average macroelements?
1. 80% 2. 20 % 3. 40% 4. 98%
5. Cells do not synthesize organic substances, but use ready-made ones
1. autotrophs 2. heterotrophs
3. prokaryotes 4. eukaryotes
6. One of the functions of the cell center
1. Formation of the spindle
2.Formation of the nuclear envelope
3.Management of protein biosynthesis
4.Movement of substances in the cell
7. Occurs in lysosomes
1.Protein synthesis
2.Photosynthesis
3. Breakdown of organic substances
4. Chromosome conjugation
8.
characteristics | |
1 Plasma membrane | |
2 Core | B. Protein synthesis. |
3 Mitochondria | B. Photosynthesis. |
4 Plastids | |
5 Ribosomes | |
6 EPS | E. Non-membrane. |
7 Cell center | G. Synthesis of fats and carbohydrates. |
8 Golgi complex | 3. Contains DNA. |
9 vacuole | I. Single membrane |
10 Lysosomes | M. Double membrane. A. Only plants have it. P. Only plants have it. |
9. Membranes and channels of the granular endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carry out the synthesis and transport of:
1. proteins 2. lipids
3. carbohydrates 4. nucleic acids.
10. In the tanks and vesicles of the Golgi apparatus:
1. secretion of proteins
2. protein synthesis, secretion of carbohydrates and lipids
3. synthesis of carbohydrates and lipids, secretion of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
4. synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates, secretion of lipids and carbohydrates.
11.The cell center is present in cells:
1. all organisms 2. only animals
3. only plants 4. all animals and lower plants.
Second part
B-1 Which cell structures undergo the greatest changes during the process? mitosis?
1) nucleus 4) lysosomes
2) cytoplasm 5) cell center
3) ribosomes 6) chromosomes
B-3 Establish a correspondence between the metabolic feature and the group of organisms for which it is characteristic.
FEATURE ORGANISMS
a) release of oxygen into the atmosphere 1) autotrophs
b) use of food energy for ATP synthesis 2) heterotrophs
c) use of ready-made organic substances
d) synthesis of organic substances from inorganic ones
e) use of carbon dioxide for nutrition
AT 4. Establish a correspondence between the process occurring in the cell and the organelle for which it is characteristic.
ORGANOID PROCESS
A) reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose 1) mitochondria
B) ATP synthesis during respiration 2) chloroplast
B) primary synthesis of organic substances
D) conversion of light energy into chemical energy
D) the breakdown of organic substances into carbon dioxide and water.
Test on the topic: « Cellular structure of organisms"
1. Cell membranes consist of:
1. plasmalemma (cytoplasmic membrane)
2. plasma membranes in animals and cell walls in plants
3. cell walls
4. plasmalemmas in animals, plasmalemmas and cell walls in plants.
2 .The functions of “power stations” are performed in the cage:
1 . ribosomes
2 . mitochondria
3 . cytoplasm
4 . vacuoles
3 .Organoid involved in cell division:
1 . ribosomes
2 . plastids
3 . Mitochondria
4 .cell center
4. Cells that synthesize organic substances from inorganic ones
1. autotrophs
2. heterotrophs
3. prokaryotes
4. eukaryotes
5. Science that studies the structure and functioning of cells
1.Biology 2.Cytology
3.Histology 4.Physiology
6.Non-membrane cell organelle
1. Cell center 2. Lysosome
3. Mitochondria 4. Vacuole
7.
Distribute the characteristics according to the cell organelles (put letters
corresponding to the characteristics of the organoid, opposite the name of the organoid).
characteristics | |
Plasma membrane | A. Transport of substances throughout the cell. |
Core | B. Protein synthesis. |
Mitochondria | B. Photosynthesis. |
Plastids | D. Movement of organelles throughout the cell. |
Ribosomes | D. Storage of hereditary information. |
EPS | E. Non-membrane. |
Cell center | G. Synthesis of fats and carbohydrates. |
Golgi complex | 3. Contains DNA. |
vacuole | I. Single membrane |
Lysosomes | K. Providing the cell with energy. L. Self-digestion of cells and intracellular digestion. M. Double membrane. N. Communication of the cell with the external environment. A. Only plants have it. P. Only plants have it. |
8. The main storage carbohydrate in animal cells:
1. starch 2. glucose 3. glycogen 4. fat
9. Membranes and channels of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carry out the synthesis and transport of:
1 proteins and carbohydrates 2 lipids 3 fats and carbohydrates 4 nucleic acids
10.Lysosomes are formed on:
1. channels of smooth EPS
2. channels of rough EPS
3. tanks of the Golgi apparatus
4. inner surface of the plasmalemma.
11. Microtubules of the cell center participate in the formation of:
1. only the cytoskeleton of the cell
2. spindles
3. flagella and cilia
4. cell cytoskeleton, flagella and cilia.
Second part
B-1. The basic principles of cell theory allow us to conclude that
1)biogenic migration of atoms
2) relatedness of organisms
3) the origin of plants and animals from a common ancestor
4) the appearance of life about 4.5 billion years ago
5) similar structure of cells of all organisms
6) the relationship between living and inanimate nature
B-3 Establish a correspondence between the structure, function of cell organelles and their type.
STRUCTURE, FUNCTIONS ORGANOIDS
B) provides oxygen formation
D) ensures the oxidation of organic substances
ANSWERS
V-1 1-2, 2-1, 3-2, 4-4, 5-2, 6-1, 7-3, 8-1n, 2d, 3k, 4mo, 5b, 6zh, 7e, 8a, 9gp ,10l; 9-1,10-3,11-4
V-1 156; V-2 256; B-3 12211; B-4 21221.
B-2 1-4, 2-2, 3-4, 4-1,5-2, 6-1, 7-1n, 2d, 3k, 4mo, 5b, 6zh, 7e, 8a, 9gp, 10l; 8-3, 9-3, 10-3,11-2
V-1 235; V-2 346; V-3 21212; B-4 246.
Tasks with solutions
1. Cells of prokaryotes, just like eukaryotes, have
1. Mitochondria
2. Plasma membrane
3. Cellular center
4. Digestive vacuoles
Explanation: Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane organelles (such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi complex, etc.), but nevertheless have a plasma membrane that surrounds the cell.
The correct answer is 2.
2. Prokaryotes include cells
1. Animals
2. Cyanobacteria
3. Mushrooms
4. Plants
Explanation: Prokaryotes include all bacteria; eukaryotes include animals, fungi and plants. But blue-green algae - cyanobacteria - have a prokaryotic structure. The correct answer is 2.
3. Eukaryotes are organisms in whose cells
1. Mitochondria are missing
2. Nucleoli are located in the cytoplasm
3. Nuclear DNA forms chromosomes
4. No ribosomes
Explanation: eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain membrane organelles, as well as ribosomes - organelles responsible for the final stage of protein synthesis, and the nucleoli are located inside the nucleus, and not in the cytoplasm (as in prokaryotes). The correct answer is 3.
4. It consists of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose and phosphoric acid residues.
1. RNA nucleotide
2. DNA nucleotide
3. tRNA
4. mRNA
Explanation: DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid because it contains, among other things, deoxyribose (that is, ribose without one oxygen). The correct answer is 2.
5. In a DNA molecule, the number of nucleotides with cytosine is 15% of total number. What is the percentage of nucleotides containing adenine in this molecule?
1. 15% 2. 30% 3. 35% 4. 85%
Explanation: According to the principle of complementarity, adenine is connected by two bonds (in DNA) to thymine, and cytosine is connected by three bonds to guanine. This means that the number of nucleotides with cytosine is equal to the number of molecules with guanine and their sum is 30%, 70% remains for the remaining nucleotides, but since they are equal in number, we can divide by two and get the number of nucleotides with adenine (which is equal to the number of nucleotides with thymine). The correct answer is 3.
Tasks for independent solution
1. What protein function is based on the ability of their molecules to change their structure?
1. Energy
2. Information
3. Contractile
4. Storage
Answer: 3.
2. Proteins that can accelerate chemical reactions perform a function in the cell
1. Hormonal 2. Signaling 3. Enzymatic 4. Informational
Answer: 3.
3. Protein molecules that can shorten and stretch perform the function
1. Motor 2. Signal 3. Structural 4. Transport
Answer: 1.
4. What substances perform the functions of biocatalysts in the body?
1. Disaccharides 2. Hormones 3. Enzymes 4. Antibodies
Answer: 3.
5. Where is rRNA synthesized?
1. On the surface of EPS
2. In the cell center
3. In the core
4. In ribosomes
Answer: 3.
6. What function do proteins perform in a cell that accelerate chemical reactions?
1. Construction
2. Signal
3. Catalytic
4. Information
Answer: 3.
7. The ability of the plasma membrane to surround a solid food particle and move it into the cell is the basis of the process
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis
3. Phagocytosis
4. Pinocytosis
Answer: 3.
8. On the membranes of which cell organelles are enzymes involved in energy metabolism located?
1. Chloroplasts
2. Golgi complex
3. Mitochondria
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 3.
9. The similarity between mitochondria and chloroplasts lies in what happens in them
1. Cellular respiration
2. Synthesis of organic substances
3. Synthesis of ATP molecules
4. Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
Answer: 3.
10. The formation of lysosomes and the growth of the plasma membrane occur due to the activity
1. Vacuoles
2. Cellular center
3. Golgi complex
4. Plastid
Answer: 3.
11. The endoplasmic reticulum is formed
1. Plasma membrane
2. Microtubules
3. Nuclear membrane
4. Mitochondria membrane
Answer: 1.
12. The cell membrane consists of a double layer
1. Phospholipids and mosaic embedded protein molecules
2. Proteins coated on the outside with phospholipids
3. Proteins, between which there is one layer of phospholipids
4. Phospholipids, between which there is one layer of protein
Answer: 1.
13. What cell organelles can be formed from the terminal vesicles of the Golgi complex?
1. Lysosomes
2. Mitochondria
3. Plastids
4. Ribosomes
Answer: 1.
14. All cell organelles are located in
1. Cytoplasm 2. Golgi complex 3. Nucleus 4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 1.
15. The endoplasmic reticulum can be recognized in a cell by its
1. A system of interconnected cavities with bubbles at the ends
2. The many grains located in it
3. A system of interconnected branched tubules
4. Numerous cristae on the inner membrane
Answer: 3.
16. In the Golgi complex occurs
1. ATP formation
2. Oxidation of organic substances
3. Accumulation of substances synthesized in the cell
4. Synthesis of protein molecules
Answer: 3.
17. What function does the cell center perform in a cell?
1. Takes part in mitotic division
2. Is a repository of hereditary information
4. Is the center of template synthesis of ribosomal RNA
Answer: 1.
18. On the membranes of which cell organelles are ribosomes located?
1. Chloroplasts
2. Golgi complex
3. Lysosome
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 4.
19. The endoplasmic reticulum in the cell performs the function
1. DNA synthesis
2. mRNA synthesis
3. Transport of substances
4. Formation of ribosomes
Answer: 3.
20. Each function in a cell is performed by the cell center?
1. Takes part in cell division
2. Regulates metabolic processes in the cell
3. Responsible for protein biosynthesis
4. Is the center of template RNA synthesis
Answer: 1.
21. Has its own DNA
1. Golgi complex
2. Lysosome
3. Endoplasmic reticulum
4. Mitochondria
Answer: 4.
22. What organelles are involved in the packaging and removal of substances synthesized in the cell?
1. Endoplasmic reticulum
2. Vacuoles
3. Lysosomes
4. Golgi apparatus
Answer: 4.
23. Which cell organelles contain a wide variety of enzymes involved in the breakdown of biopolymers into monomers?
1. In chloroplasts
2. In lysosomes
3. In ribosomes
4. In mitochondria
Answer: 2.
24. Formed in the nucleus
1. Mitochondria
2. Chloroplasts
3. Lysosome enzymes
4. Ribosomal subunits
Answer: 4.
25. Are the following statements about lipid synthesis true?
A. Lipid synthesis in the cell is associated with smooth ER.
B. Lipid synthesis in the cell is associated with lysosomes and ribosomes.
1. Only A is correct
2. Only B is correct
3. Both judgments are correct
4. Both judgments are wrong.
Answer: 1.
26. In the cell, the breakdown of proteins into amino acids with the participation of enzymes occurs in
1. Mitochondria
2. Lysosomes
3. Golgi complex
4. Nucleoli
Answer: 2.
27. The process of denaturation of a protein molecule is reversible if the bonds are not broken
1. Hydrogen
2. Peptide
3. Hydrophobic
4. Disulfide
Answer: 2.
28. In a DNA molecule, the number of nucleotides with thymine is 20% of the total number. What is the percentage of nucleotides with cytosine in this molecule?
1. 30%
2. 40%
3. 60%
4. 80%
Answer: 1.
29. Water participates in the thermoregulation of living organisms thanks to
1. Ability to dissolve substances
2.High heat capacity
3. Catalytic properties
4. Small molecular sizes
Answer: 2.
30. In animal cells, lipids are synthesized in
1. Ribosomes
2. Lysosomes
3. Endoplasmic reticulum
4. Core
Answer: 3.
31. The function of carbohydrates in the cell -
1. Catalytic
2. Energy
3. Storage of hereditary information
4. Participation in protein biosynthesis
Answer: 2.
32.V aquatic environment cells undergo many chemical reactions because water
1. Is a solvent for many chemical compounds
2. Has a large heat capacity
3. Has fluidity and mobility
4. Serves as the main cell filler
Answer: 1.
33. Sperm in mammals differs from sperm in flowering plants.
1. Haploid set of chromosomes
2. Large sizes
3. Mobility
4. Availability of nutrients
Answer: 3.
34. The similarity of eukaryotic cells lies in the presence of
1. Organoid movement
2. Fiber casings
3. Cell membrane
4. Chitin shells
Answer: 3.
35. The sperm, unlike the egg, does not have
1. Detached core
2. Cell membrane
3. Nutrient reserves
4. Mitochondria
Answer: 3.
36. Cells with the help of which children inherit the characteristics of their parents -
1. Reproductive 2. Somatic 3. Nervous 4. Blood cells
Answer: 1.
37. Prokaryotic cells, unlike eukaryotic cells, do not have
1. Chromosome
2. Cell membrane
3. Nuclear membrane
4. Plasma membrane
Answer: 3.
38. DNA molecules are found in chromosomes, mitochondria and chloroplasts of cells
1. Bacteria
2. Eukaryote
3. Prokaryote
4. Bacteriophages
Answer: 2.
39. Circular DNA is located directly in the cytoplasm of the cell in
1. Dysenteric amoeba
2. Chlamydomonas
3. Azotobacteria
4. Euglena green
Answer: 3.
40. Why are single-celled animals classified as eukaryotes?
1. They have a formed core
2. Oxidize organic substances and store ATP
3. Proteins are synthesized on ribosomes
Answer: 1.
41. A derivative of the plasma membrane - glycocalyx - is present on the surface of cells
1. Mushrooms
2. Animals
3. Viruses
4. Bacteriophages
Answer: 2.
42. Haploid nuclei contain cells
1. Rhizomes of bracken
2. Sperm cells of a flowering plant
3. Brown algae zygote
4. Coniferous roots
Answer: 2.
43. The frequency of crossing over between two genes on a chromosome is determined
1. Dominance of one of the genes
2. Dominance of both genes
3. Differences in gene dominance
4. Distance between genes
Answer: 4.
44. Mitosis does not occur in prophase
1. Dissolution of the nuclear membrane
2. Formation of the spindle
3. DNA duplication
4. Dissolution of nucleoli
Answer: 3.
45. In interphase before mitosis in a cell
1. Chromosomes line up in the equatorial plane
2. Chromosomes move to the poles of the cell
3. The number of DNA molecules is halved
4. The number of DNA molecules doubles
Answer: 4.
46. Biological significance meiosis consists of
1. Preservation of the karyotype of the species during sexual reproduction
2. Formation of cells with double the number of chromosomes
3. The appearance of a large number of somatic cells
4. Providing cells with organic substances
Answer: 1.
47. The divergence of homologous chromosomes to the cell poles occurs in
1. Anaphase of meiosis 1
2. Metaphase of meiosis 1
3. Metaphase of meiosis 2
4. Anaphase of meiosis 2
Answer: 1.
48. During the process of cell division, the most significant transformations undergo
1. Ribosomes
2. Chromosomes
3. Mitochondria
4. Lysosomes
Answer: 2.
49. There are 20 chromosomes in the nuclei of cells in the intestinal mucosa of a vertebrate animal. What number of chromosomes will the zygote nucleus of this animal have?
1. 10
2. 20
3. 30
4. 40
Answer: 2.
50. The formation of two chromatids in chromosomes is based on the process
1. DNA self-duplicating
2. mRNA synthesis
3. DNA helixation
4. Formation of ribosomes
Answer: 1.
51. Conjugation and crossing over are of great importance for evolution, as they contribute
1. Preservation of the gene pool of the population
2. Changes in population size
3. Increasing the viability of offspring
4. The emergence of new combinations of traits in the population
Answer: 4.
52. The first phase of meiosis is characterized by the process
1. Conjugation
2. Protein biosynthesis
3. Replications
4. ATP synthesis
Answer: 1.
53. The formation of two cells with a diploid set of chromosomes from one mother cell is characteristic of the process
1. Mitosis
2. Crossing over
3. Maturation of the egg
4. Meiosis
Answer: 1.
54. The chromosome set in a woman’s somatic cells consists of
1. 44 autosomes and two X chromosomes
2. 44 autosomes and two Y chromosomes
3. 44 autosomes and X- and Y-chromosomes
4. 22 pairs of autosomes and X- and Y-chromosomes
Answer: 1.
55. Thanks to meiosis and fertilization
1. A constant number of chromosomes is maintained over generations
2. The likelihood of mutations in the offspring is reduced
3. The number of chromosomes changes from generation to generation
4. The phenotype of individuals in populations of the species is preserved
Answer: 1.
56. Reducing the number of chromosomes by half, the formation of cells with a haploid set of chromosomes occurs in the process
1. Mitosis
2. Crushing
3. Fertilization
4. Meiosis
Answer: 4.
57. Endosperm cells of flowering plants have a set of chromosomes
1.n
2.2n
3.3n
4.4n
Answer: 3.
58. In the body, mitosis is the basis
1. Gametogenesis
2. Growth and development
3. Metabolism
4. Self-regulation processes
Answer: 2.
59. The reduction in the number of chromosomes and DNA molecules by half during the process of meiosis is due to the fact that
1. The second division of meiosis is not preceded by DNA synthesis
2. The first division of meiosis is not preceded by DNA synthesis
3. In the first division of meiosis, chromosome conjugation occurs
4. Crossing over occurs in the first division of meiosis
Answer: 1.
60. The process of cell division consumes the energy of ATP molecules, which are synthesized in
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Interphase
4. Anaphase
Answer: 3.
61. One interphase and two successive divisions are characteristic of progress
1. Fertilization
2. Cleavage of the zygote
3. Mitosis
4. Meiosis
Answer: 4.
62. How can we explain the constancy of the number of chromosomes in individuals of the same species?
1. Diploidy of the organism
2. The process of cell division
3. Haploidy of organisms
4. The processes of meiosis and fertilization
Answer: 4.
63. During the process of meiosis, homologous chromosomes diverge to different poles of the cell in
1. Metaphase of the first division
2. Second generation metaphase
3. Anaphase of the first division
4. Anaphase of the second division
Answer: 3.
64. Chromosome conjugation is characteristic of the process
1. Fertilization
2. Metaphases of the second meiotic division
3. Anaphases of mitosis
4. Prophases of the first meiotic division
Answer: 4.
65. Cells are formed through meiosis
1. Muscular
2. Epithelial
3. Sexual
4. Nervous
Answer: 3.
66. The nucleus in a cell can be viewed with a light microscope during
1. Metaphases
2. Prophases
3. Interphases
4. Anaphases
Answer: 3.
67. Thanks to conjugation and crossing over, meiosis occurs
1. Reducing the number of chromosomes by half
2. Double the number of chromosomes
3. Exchange genetic information between homologous chromosomes
4. Increase in the number of female and male reproductive cells
Answer: 3.
68. How many DNA molecules are contained in each chromosome at the end of interphase?
1. One
2. Two
3. Three
4. Four
Answer: 2.
69. The number of chromosomes during sexual reproduction in each generation would double if the process had not been formed during evolution
1. Mitosis
2. Meiosis
3. Fertilization
4. Pollination
Answer: 2.
70. A sign characteristic of both the egg and the sperm -
1. Diploid set of chromosomes
2. Small sizes and mobility
3. Small size and immobility
4. Haploid set of chromosomes
Answer: 4.
71. The process of division, as a result of which from the original diploid cell four haploid cells are formed, called
1. Mitosis
2. Crushing
3. Fertilization
4. Meiosis
Answer: 4.
72. Divergence of sister chromosomes occurs in
1. Anaphase of meiosis 1
2. Metaphase of meiosis 1
3. Metaphase of meiosis 2
4. Anaphase of meiosis 2
Answer: 4.
73. What does chromosome spiralization lead to at the beginning of mitosis?
1. Shortening and thickening of chromosomes
2. Active participation of chromosomes in protein biosynthesis
3. Doubling of DNA molecules
4. Transcriptions and translations
Answer: 1.
74. What role do chromosomes play in a cell?
1. Act as biocatalysts
2. Store hereditary information
3. Participate in the assembly of proteins on ribosomes
4. Participate in the synthesis of carbohydrates
Answer: 2.
75. Independent divergence of homologous chromosomes in meiosis promotes
1. The occurrence of chromosomal mutations
2. Changes in the norm of reaction of signs of the future organism
3. Formation of new combinations of characteristics
4. The emergence of modification variability
Answer: 3.
76. What is characteristic of somatic cells of vertebrates?
1. When fused, they form a zygote
2. They have the same shape
3. Participate in sexual reproduction
4. Have a diploid set of chromosomes
Answer: 4.
77. As a result of what process do gametes mature in animals?
1. Mitosis
2. Meiosis
3. Fertilization
4. Crushing
Answer: 2.
78. Which of the following animals produces more eggs during their life?
1. Domestic dog
2. Rock pigeon
3. House mouse
4. Cod fish
Answer: 4.
79. What phenomenon disrupts the cohesion of genes localized on the same chromosome?
1. Combinative variability
2. Crossing over
3. Modification
4. Conjugation
Answer: 2.
80. The egg is the smallest size
1. Human
2. Frogs
3. Cod
4. Lizards
Answer: 1.
81. The reason for the constancy of the number of chromosomes in the offspring during sexual reproduction is the processes
1. Meiosis and fertilization
2. Transcriptions and translations
3. Conjugation and crossing over
4. Metabolism and energy
Answer: 1.
82. Are the following statements about mitosis true?
A. As a result of mitosis, cells are formed with a set of chromosomes identical to the mother cell.
B. Daughter cells with a reduced set of chromosomes are formed as a result of meiosis.
1. Only A is correct
2. Only B is correct
3. Both judgments are correct
4. Both judgments are wrong.
Answer: 3.
83. How does mitosis differ from meiosis?
1. Two successive divisions occur
2. One division occurs, consisting of four phases
3. Two daughter cells are formed, identical to the mother one
4. Four haploid cells are formed
5. Homologous chromosomes diverge to the cell poles
6. Only sister chromatids move to the cell poles
Answer: 236.
84. Establish the sequence of changes that occur to chromosomes during mitosis.
1. Division of the centromere and the formation of their chromosome chromatids
2. Divergence of sister chromosomes to different poles of the cell
3. Arrangement of chromosomes in the equatorial plane
4. Free arrangement of chromosomes in the cytoplasm
5. Attachment of spindle filaments to chromosomes
Answer: 45312.
85. Animal germ cells, unlike somatic ones,
2. Have a set of chromosomes identical to the maternal one
3. Formed by mitosis
4. Formed during the process of meiosis
5. Participate in fertilization
6. They form the basis for the growth and development of the body
Answer: 145.
86. Are the following statements true about prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. All prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane and ribosomes.
B. The nuclear substances of cyanobacteria are located in the cytoplasm and are not surrounded by a membrane, therefore they are classified as prokaryotes.
1. Only A is correct
2. Only B is correct
3. Both judgments are correct
4. Both judgments are wrong.
Answer: 3.
87. The cells of plant organisms, unlike animals, contain
1. Chloroplasts
2. Mitochondria
3. Nucleus and nucleolus
4. Vacuoles with cell sap
5. Cell wall made of cellulose
6. Ribosomes
Answer: 145
88. Establish a correspondence between the feature of an object and the form of life for which it is characteristic.
Object attribute Life form
A. Presence of ribosomes 1. Non-cellular (viruses)
B. Lack of plasma membrane 2. Cellular (bacteria)
B. They do not have their own metabolism
D. Most are heterotrophs
D. Reproduction only in host cells
E. Reproduction by cell division
Answer: 211212
89. Establish a correspondence between the characteristics of a cell and its type
Characteristics Type of cell
A. Lack of a formed core 1. Animal
B. Does not have a cell wall 2. Bacterial
B. Has one DNA molecule
D. Contains several chromosomes
D. Contains mitochondria and Golgi complex
E. DNA is located in the cytoplasm
Answer: 212112.
90. Metabolism and energy conversion occurring in the cells of all living organisms indicate that the cell is a unit
1. Structures of organisms
2. Life activities of organisms
3. Reproduction of organisms
4. Genetic information
Answer: 2.
91. “Cells reproduce by dividing them...! - this is the position of the theory
1. Ontogenesis
2. Cellular
3. Phylogeny
4. Mutation
Answer: 2.
92. The cells of all organisms contain proteins, which serves as evidence
1. Unity of living and inanimate nature
2. Unity organic world
3. Evolution of the organic world
4. Adaptation of organisms to the environment
Answer: 2
93. Life processes take place in a cell, so it is considered as a unit
1. Reproduction
2. Buildings
3. Functional
4. Genetic
Answer: 3.
94. Cell theory summarizes ideas about
1. The diversity of the organic world
2. Relationship of organisms of different kingdoms
3. Historical development of organisms
4. Unity of living and inanimate nature
Answer: 2.
95. From the above statements, indicate the position of the cell theory
1. A zygote is formed during the process of fertilization
2. Meiosis produces cells with a haploid set of chromosomes
3. Cells are formed as a result of division of the original cell
4. Somatic cells are formed as a result of mitosis
Answer: 3.
96. Indicate the position of the cell theory
1. Fertilization is the process of fusion of male and female cells
2. During the process of meiosis, allelic genes end up in different germ cells
3. The cells of all organisms are similar in chemical composition and structure
4. Ontogenesis is the development of an organism from the moment of fertilization of the egg until the death of the organism
Answer: 3.
97. What theory substantiated the position about the structural and functional unit of living things?
1. Phylogeny
2. Cellular
3. Evolution
4. Embryogenesis
Answer: 2.
98. Testifies to the unity of the organic world
1. Similarity of individuals of the same species
2. Cellular structure of organisms
3. Life of organisms in natural communities
4. The existence of diversity of species in nature
Answer: 2.
99. Organisms of plants, animals, fungi and bacteria consist of cells - this indicates
1. Unity of the organic world
2. The diversity of the structure of living organisms
3. Relationships between organisms and their environment
4. The complex structure of living organisms
Answer: 1.
100. Testifies to the unity of the organic world
1. The presence of a nucleus in the cells of living organisms
2. Cellular structure of organisms of all kingdoms
3. Systematics of organisms of all kingdoms
4. Diversity of organisms inhabiting the Earth
Answer: 2.
101. The cell is considered a unit of growth and development of organisms, since
1. It has a complex structure
2. The body is made up of tissues
3. Cells are capable of dividing
4. Gametes are formed by meiosis
Answer: 3.
102. Organisms are made up of cells, so a cell is considered a unit
1. Development
2. Reproduction
3. Buildings
4. Life activities
Answer: 3.
103. The unit of reproduction of organisms is
1. Chromosome
2. Gene
3. Cage
4. DNA
Answer: 3.
104. In the cell, the breakdown of proteins into amino acids with the participation of enzymes occurs in
1. Mitochondria
2. Lysosomes
3. Golgi complex
4. Nucleoli
Answer: 2.
105. Carbon dioxide is used as a carbon source in metabolic reactions such as
1. Lipid synthesis
2. Nucleic acid synthesis
3. Chemosynthesis
4. Protein synthesis
Answer: 3.
106. The energy of sunlight is converted into the energy of chemical bonds in cells
1. Phototrophs
2. Chemotrophs
3. Heterotrophs
Answer: 1.
107. The synthesis of ATP molecules occurs in the process
1. Protein biosynthesis
2. Carbohydrate synthesis
3. Preparatory stage energy metabolism
4. Oxygen stage of energy metabolism
Answer: 4.
108. Photosynthesis first appeared in
1. Cyanobacteria
2. Psilophytes
3. Unicellular algae
4. Multicellular algae
Answer: 1.
109. In the oxygen-free stage of energy metabolism, molecules are broken down
1. Glucose to pyruvic acid
2. Protein to amino acids
3. Starch to glucose
4. Pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water
Answer: 1.
110. Oxidation of organic substances with the release of energy in the cell occurs in the process
1. Biosynthesis
2. Breathing
3. Discharge
4. Photosynthesis
Answer: 2.
111. The synthesis of ATP molecules does not occur in the process
1. Transport of substances into the cell through the membrane
2. Oxygen stage of energy metabolism
3. Oxygen-free stage of energy metabolism
4. Light phase of photosynthesis
Answer: 1.
112. Energy exchange cannot occur without plastic, which supplies the necessary for chemical reactions
1. Enzymes
2. Inorganic substances
3. ATP molecules
4. Oxygen molecules
Answer: 1.
113. The transition of electrons to a higher energy level occurs in the light phase of photosynthesis in molecules
1. Chlorophyll
2. Water
3. Carbon dioxide
4. Glucose
Answer: 1.
114. The process of splitting biopolymers into monomers with the release of a small amount of energy in the form of heat is characteristic of
1. Preparatory stage of energy metabolism
2. Oxygen-free stage of energy metabolism
3. Oxygen stage of energy metabolism
4. Fermentation process
Answer: 1.
115. What process does not occur during the light phase of photosynthesis?
1. ATP synthesis
2. Synthesis of NADP-2H
3. Photolysis of water
4. Glucose synthesis
Answer: 4.
116. The relationship between plastic and energy metabolism is manifested in the fact that
1. Energy metabolism supplies energy for plastic
2. Energy metabolism supplies oxygen to the plastic
3. Plastic exchange supplies minerals for energy
4. Plastic metabolism supplies energy for the energetic
Answer: 1.
117. Fungal cells during intensive growth receive energy in the process
1. Lipid synthesis
2. Carbohydrate synthesis
3. Breakdown of mineral salts
4. Oxidation of organic substances
Answer: 4.
118. Oxygen molecules during photosynthesis are formed due to the decomposition of molecules
1. ATP
2. Glucose
3. Carbon dioxide
4. Water
Answer: 4.
119. How many ATP molecules are synthesized by a cell at the stage of anaerobic breakdown of one glucose molecule?
1. 18
2. 2
3. 36
4. 38
Answer: 2.
120. Are the following statements about metabolism in a cell correct?
A. The breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid during energy metabolism occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell
B. During the oxidation of pyruvic acid, ATP molecules are stored greatest number energy
1. Only A is correct
2. Only B is correct
3. Both judgments are correct
4. Both judgments are wrong.
Answer: 3.
121. Are the following statements about metabolism in a cell correct?
A. Information about the sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule is encrypted using a genetic code.
B. The sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule is determined by tRNA molecules.
1. Only A is correct
2. Only B is correct
3. Both judgments are correct
4. Both judgments are wrong.
Answer: 1.
122. Establish a correspondence between the sign of energy metabolism and its stages.
Sign of energy exchange Stage of exchange
A. Pyruvic acid is broken down 1. Glycolysis
acid to carbon dioxide and water 2. Oxygen splitting
B. Glucose is broken down into
pyruvic acid
B. Two ATP molecules are synthesized
D. 36 ATP molecules are synthesized
D. Occurs in mitochondria
E. Occurs in the cytoplasm
Answer: 211221.
123. Install correct sequence photosynthesis processes
1. Converting solar energy into ATP energy
2. Formation of excited electrons of chlorophyll
3. Carbon dioxide fixation
4. Starch formation
5. Conversion of ATP energy into glucose energy
Answer: 21354.
124. What processes are caused by the energy of sunlight in a leaf?
1. Formation of molecular oxygen as a result of the decomposition of water
2. Oxidation of pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water
3. Synthesis of ATP molecules
4. Breakdown of biopolymers to monomers
5. Breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid
6. Formation of hydrogen ions
Answer: 136.
125. Establish the sequence of processes occurring at each stage of energy metabolism in the human body
1. Breakdown of starch to glucose
2. Complete oxidation of pyruvic acid
3. Entry of monomers into the cell
4. Glycolysis, the formation of two ATP molecules
Answer: 1342.
126. Establish a correspondence between the process occurring in the cell and the organelle in which it occurs.
Organoid Process
A. Reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose 1. Mitochondria
B. ATP synthesis during respiration 2. Chloroplast
B. Primary synthesis of organic substances
D. Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
D. Breakdown of organic substances to
carbon dioxide and water
Answer: 21221
127. What is the sequence of energy metabolism processes in a cell?
1. Breakdown of starch to monomers
2. Entry of organic polymers into lysosomes
3. Breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid
4. Entry of pyruvic acid into mitochondria
5. Formation of carbon dioxide and water
Answer: 21345.
128. mRNA molecules carry hereditary information from
1. Cytoplasm to the nucleus
2. One cell to another
3. Nuclei to mitochondria
4. Nuclei to ribosomes
Answer: 4.
129. The genetic code is the same for organisms of all kingdoms of living nature, in which it is manifested
1. Redundancy
2. Versatility
3. Unambiguity
4. Degeneracy
Answer: 2.
130. Choose the correct sequence of information transfer in the process of protein synthesis in the cell.
1. DNA → mRNA → protein
2. DNA → tRNA → protein
3. rRNA → tRNA → protein
4. rRNA → DNA → tRNA → protein
Answer: 1.
131. Information about the sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule is copied in the nucleus from DNA molecule to molecule
1. ATP
2. rRNA
3. tRNA
4. mRNA
Answer: 4.
132. The genetic code is universal, since
1. Each amino acid is encoded by a triple of nucleotides
2. The location of an amino acid in a protein molecule is determined by different triplets
3. It is the same for all creatures living on Earth
4. Several triplets code for one amino acid
Answer: 3.
133. The same amino acid corresponds to a TGA triplet on DNA and a tRNA anticodon -
1. UGA
2. TsUG
3. ACU
4. AHA
Answer: 1.
134. A section of DNA containing information about one polypeptide chain, - This
1. Gene
2. Codon
3. Triplet
4. Chromosome
Answer: 1.
135. The matrix for the translation process is a molecule
1. DNA
2. tRNA
3. mRNA
4. rRNA
Answer: 3.
136. How many nucleotides in a gene encode the sequence of 60 amino acids in a protein molecule?
1. 60
2. 120
3. 180
4. 240
Answer: 3.
137. A protein consists of 150 amino acid residues. How many nucleotides are there in the gene region that encodes the primary structure of this protein?
1. 75
2. 150
3. 300
4. 450
Answer: 4.
138. The same amino acid corresponds to the anticodon AAG on tRNA and the triplet on DNA -
1. AAG
2. TCU
3. Central Control Center
4. UTC
Answer: 1.
139. Molecules of what substance are intermediaries in the transfer of information about the primary structure of a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome?
1. DNA
2. tRNA
3. ATP
4. mRNA
Answer: 4.
140. Choose the correct position characterizing the “unambiguity of the genetic code.”
1. Each triplet corresponds to only one amino acid
2. A gene in a DNA chain has a strictly fixed reading start
3. The genetic code is the same for all organisms living on Earth
4. One amino acid corresponds to several triplets
Answer: 1.
141. Establish the sequence in which the process of DNA reduplication occurs.
1. Unwinding the DNA molecule helix
2. Connection of nucleotides by the enzyme DNA polymerase
3. Separating one chain from another into parts of a DNA molecule
4. Attaching complementary nucleotides to each DNA strand
5. Formation of two DNA molecules from one
Answer: 13425.
142. Establish the sequence of processes occurring in an interphase cell.
1. mRNA is synthesized on one of the DNA strands
2. Two strands of a section of a DNA molecule are separated under the influence of enzymes
3. mRNA moves into the cytoplasm
4. Protein synthesis occurs on mRNA, which serves as a template.
Answer: 2134.
143. Which of the following processes relate to protein biosynthesis
1. The ribosome is strung on mRNA
2. Organic substances accumulate in the cavities and tubules of the ER
3. tRNAs attach amino acids and deliver them to the ribosome
4. Before cell division, two chromatids are formed from each chromosome
5. Two amino acids attached to the ribosome interact with each other to form a peptide bond
6. During the oxidation of organic substances, energy is released
Answer: 135.
144. What are the features of protein biosynthesis reactions in a cell?
1. Reactions are matrix in nature: protein is synthesized on mRNA
2. Reactions occur with the release of energy
3. Chemical reactions consume the energy of ATP molecules
4. Reactions are accompanied by the synthesis of ATP molecules
5. Acceleration of reactions is carried out by enzymes
6. Protein synthesis occurs on the inner membrane of mitochondria
Answer: 135.
145. During the process of meiosis,
1. Formation of germ cells
2. Formation of prokaryotic cells
3. Reducing the number of chromosomes by half
4. Preservation of the diploid set of chromosomes
5. Formation of two daughter chromosomes
6. Development of four haploid cells
Answer: 136.
146. What processes occur in the prophase of the first meiotic division?
1. Formation of two nuclei
2. Divergence of homologous chromosomes
3. Formation of the metaphase plate
4. Bringing together homologous chromosomes
5. Exchange of sections of homologous chromosomes
6. Chromosome spiralization
Answer: 456.
147. Establish a correspondence between the feature of cell division and the method of division for which it is characteristic.
Features of division Method of division
A. Two diploids are formed 1. Mitosis
daughter cells 2. Meiosis
B. Provides maturation
gametes in animals
B. Maintains constancy of number
chromosomes in cells
D. Recombination occurs
genes on chromosomes
D. Serves as a means of asexual
protozoan reproduction
Answer: 12121.
148. Establish a correspondence between the characteristic of the process and the method of cell division that it illustrates
Characteristics Method of division
A. Divergence to the poles 1. Meiosis
homologous chromosomes 2. Mitosis
B. Conjugation of homologous
chromosomes
B. Formation of four
haploid daughter cells
D. Formation of two subsidiaries
cells with the number of chromosomes,
equal to the mother cell
D. Gene exchange between
homologous chromosomes
Answer: 11121.
149. Establish a correspondence between the features of carbohydrate molecules and their type.
Features of molecules Type of carbohydrates
A. Monomer 1. Cellulose
B. Polymer 2. Glucose
B. Soluble in water
D. Insoluble in water
D. Part of the cell walls of bacteria
E. Part of the cell sap of plants
Answer: 212112.
150. Establish a correspondence between the structure and function of organic matter and its type
Structure and function Type of substance
A. Consist of the remains of molecules 1. Fats
glycerol and fatty acids 2. Proteins
B. Consist of residues of amino acid molecules
B. Protect the body from hypothermia
D. Protect the body from foreign substances
D. Refers to polymers
E. Are not polymers
Answer: 121221.
151. What structural features and properties of water molecules determine its major role in the cell?
1. Ability to form hydrogen bonds
2. The presence of energy-rich bonds in molecules
3. The polarity of its molecules
4. Ability to form ionic bonds
5. Ability to form peptide bonds
6. Ability to interact with ions
Answer: 136.
152. In what structures of eukaryotic cells are DNA molecules localized?
1. Cytoplasm
2. Core
3. Mitochondria
4. Ribosomes
5. Chloroplasts
6. Lysosomes
Answer: 235.
153. What functions does water perform in a cell?
1. Construction
2. Solvent
3. Catalytic
4. Storage
5. Transport
6. Gives the cell elasticity
Answer: 256.
154. What are the structural features and properties of protein molecules?
1. I have primary, secondary, tertiary structures
2. They look like a double helix
3. Monomers - amino acids
4. Monomers - nucleotides
5. Capable of replication
6. Capable of denaturation
Answer: 136.
155. What processes occur in the cell nucleus?
1. Formation of the spindle
2. Formation of lysosomes
3. Doubling of DNA molecules
4. Synthesis of mRNA molecules
5. Formation of mitochondria
6. Formation of ribosomal subunits
Answer: 346.
156. What general properties characteristic of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
1. Cells do not divide during life
2. Have their own genetic material
3. They are single-membrane
4. Contain oxidative phosphorylation enzymes
5. Have a double membrane
6. Participate in ATP synthesis
Answer: 256.
The tasks are taken from the collection of tasks for preparing for the Unified State Exam, edited by G. S. Kalinova.

