Thin growths on the skin. Keratomas: causes and methods of removal
Any neoplasms on the skin cause justified concern, both in terms of aesthetic discomfort and functional inconvenience, and in terms of the possibility of degeneration into a malignant tumor. These include keratomas.
What is a keratoma? This is a collective term that combines a number of specific benign neoplasms of a brownish or dark brown color, formed from cells of the superficial (horny) layer of the epidermis, which have a common mechanism of development and similar clinical manifestations.
The mechanism and causes of skin keratoma formation
At the initial stages, the neoplasm may look like a small rough erythematous (redness) spot, slightly rising above the healthy surface of the skin, slightly flaky due to flaking significant amount horny epithelium. It is easier to determine by palpation (to the touch) than visually, it can be single or multiple.
Gradually, the area of the formation increases and more and more rises above the skin. The surface of the keratoma is covered first with a yellowish, and then with a brown crust, becomes rough and can bleed when damaged.
Keratomas are formed from keratinocytes, which are the main cell type of the basal layer of the epidermis, immediately adjacent to the dermis. Keratinocytes are structurally multilayered squamous epithelium where keratin proteins are synthesized.
These cells perform a protective function and have pronounced immune qualities. As a result of division and as they mature, they move from the underlying layers of the epidermis to the overlying ones, gradually losing cell nucleus and cytoplasm, and turning into non-viable corneocytes. The latter are cells consisting only of a membrane in which keratins (80%) and lipids are enclosed.
Thus, as a result of maturation and transformation into cells of the next, more outer layer of the epidermis, keratinocytes form a structure of several layers, including the stratum corneum, and are subsequently rejected in the form of scales. After the latter are rejected, new ones rise in their place from a deeper layer.
Renewal of the skin epithelium occurs continuously. The processes of cell death and restoration in the basal layer are balanced in time. If, for some reason, the balance is disturbed on a skin area, which begins mainly after the age of 40, this leads to the formation of benign keratomas, consisting of corneocytes, and, as a result, of keratinocytes.
The maximum number of people with keratomas, regardless of gender, falls on the age of 50 to 60 years or more. At the same time, some studies report an incidence of 11% among people 20 years of age and 25% - 30 years old, over 40 years old - 15% in Britain and 45% - in Australia.

In the pathogenesis of the disease, a special role is given to the influence of long-term (depending on intensity) accumulation of the effects of ultraviolet and infrared spectra of solar radiation (especially excess), as well as ionizing and other types of electromagnetic rays. Their influence especially affects the background of age-related increase in the rate of cellular aging. These spectra affect cellular RNA and DNA of keratinocytes and provoke their tumor transformation.
The results of such a negative influence are eliminated by the antitumor defenses of the organism itself. Damaged cells become foreign and are eliminated (destroyed) through apoptosis (programmed cell death). If the body's strength is not enough for this, which occurs mainly in middle and old ages, stable genetic changes in keratinocytes and the accumulation of mutated material occur. As a result, their proliferation (growth) ceases to be controlled, and the processes of keratinization in areas of the body, especially open areas, increase dramatically.
Basically, keratomas are benign and can resolve on their own, but some of their types in 8-35% of cases can degenerate into skin cancer. In the mechanisms of transformation into cancerous tumor, in addition to the above, the disorder of the processes of interaction between cells, an increase in the function of retinoid receptors, a weakening immune mechanisms body, excessive consumption of foods high in fat (there is no exact explanation for this).
The most important predisposing factors for the occurrence of keratomas of this group:
- Congenital deficiency or absence of melanin (albinism).
- hereditary hypersensitivity skin to ultraviolet rays.
- Rare hereditary Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, characterized by specific skin lesions with hyperkeratosis, hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, dystrophic changes in teeth, nails and hair, short stature, etc.
- Hereditary Cockayne syndrome - dwarfism in combination with mental underdevelopment, hypersensitivity to UV radiation, pathological changes lens and retina, etc.
- Bloom's syndrome is a chromosomal disorder characterized by short stature, telangiectatic spots on the face, hypersensitivity to sunlight, and a predisposition to malignant neoplasms.
- The influence of physical stimuli - ultraviolet, infrared and ionizing types of radiation.
- Exposure to chemical irritants - arsenic and its derivatives, some hydrocarbon compounds, including tar.
- Drug immunosuppression with azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclosporine, urea derivatives (hydroxyurea) and other immunosuppressants.
- Use photochemically active funds(psoralens).
Types of keratomas
Depending on the advantage of certain causative factors, the following main types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Seborrheic keratoma, or senile, age-related, senile.
- Solar, or actinic.
- Follicular.
Senile keratosis
There are many clinical varieties of these most common benign epithelial tumors. They can be localized on any part of the skin, excluding the palmar and plantar surfaces. There are separate descriptions of the occurrence of foci on the conjunctiva of the eye and the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
The factors contributing to their development include mainly:
- genetic predisposition;
- prolonged and/or intense insolation;
- immune disorders;
- influence, especially when localized on the skin of the external genital organs.
Senile keratoma occurs in middle age, from about 30 years old, when the thinning of the epidermal layer reaches 10%. Among the elderly, after 50 years, its prevalence reaches 80-100%. This is due to tissue aging and increased resistance of keratinocytes to apoptosis processes. They are still more accumulate mutations, which significantly increases the risks malignant degeneration. In addition, in middle and old age, the number of enzymatically active melanocytes decreases markedly, which leads to a decrease in the barrier function of the skin against the negative effects of ultraviolet rays.
On the early stages development, the neoplasm appears as a yellowish-brown spot of an oval or rounded shape. Gradually, over time, the tumor acquires dark tones and turns into a convex, as if glued to the skin plate or plaque with clearly defined boundaries.
Age-related keratomas in people under 50 are more often solitary and are located on open areas of the body (face, neck, arms, upper divisions chest), in older people they are multiple, distributed throughout the body with the main localization in closed areas (legs, various parts of the abdomen and back).
The tumor surface has a "greasy" sheen due to excess sebum, which is why they are also called seborrheic. In addition, the surface is rough due to the presence of multiple scales and small formations, similar to papillomas. They form crusts, sometimes reaching a thickness of up to 10-20 mm. The diameter of different foci is different and also varies widely - from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Senile keratomas grow for years. During this time, their shape, degree of elevation above the skin and color often change. They take the form of a mushroom with jagged contours and a black or dark brown color with white or black patches of keratin, having a diameter of up to 1 mm. With excessive sweating, the elements can cause itching. In this case, redness, swelling, peeling of the skin around them occurs, an unpleasant odor appears.

In accordance with the histological picture, 4 forms of elements are distinguished, which are successive stages in the development of keratoma:
- spotted form, which looks like a round or oval spot up to 3-7 mm in diameter with fuzzy contours, which usually has a pinkish-yellowish color on the face, and light brown on the body; their surface is smooth or rough, and the surrounding skin is atrophic and easily gathers into wrinkles;
- nodular is a dirty yellow or dark gray formation up to 1 cm with edges raised above healthy skin; it is covered with epithelial scales, when removed, the pink surface of the tumor is exposed;
- plaque - looks like a "disk" of gray color with pronounced borders and a diameter of 5-10 mm; the surface is covered with a dense layer of horny epithelium, when scraped off, bleeding occurs;
- a tumor similar to Bowen's disease; Bowen's disease affects the elderly and is a precancerous dermatosis; a keratoma is a plaque with clear boundaries of a jagged shape 1-1.5 cm in size and with a small number of scales on the surface; the plaque itself is formed as a result of the fusion of several smaller elements; the focus has a pinkish or copper tint, and its central part, painted in brownish and grayish hues, undergoes atrophy and sinks in the process of growth; despite the similarity to Bowen's precancer, this form of keratoma rarely transforms into cancer.
Skin horn
Another skin disease that is one of the variants of senile keratosis is the skin horn. It occurs (more often in women) in the scalp, ears and on the face. The focus is formed from an already existing keratoma as a result of constant exposure to microtraumas, sunburn, infection, chemical irritants, etc. The formation has a cylindrical or conical shape, gradually increases in length, reaching a significant size, or (less often) in width. AT last case the tumor becomes round and wide, and is connected to the skin by means of a thin stalk.
Its consistency is dense, the color is brown or yellowish-brown, the surface is rough or smooth. At the base of the cutaneous horn inflammatory process in the form of a reddish corolla. The skin horn is often malignant and refers to precancerous tumors.
Senile keratomas never go away on their own. They are often injured as a result external influence or friction with clothing, which contributes to their transformation into squamous cell skin cancer or.
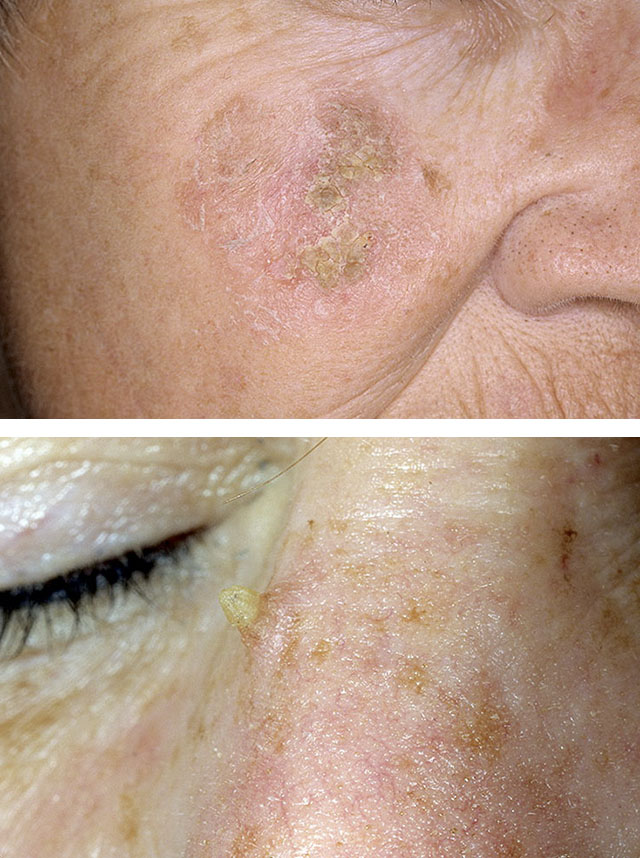
1. Actinic keratoma
2. Skin horn
actinic keratoma
This is one of the most common dermatological diseases that occurs in old age, especially in people with fair skin. For this species, the accumulation of mutations in cells is most characteristic due to the influence not so much of age itself, but of chronic long-term exposure to sunlight.
The name keratosis comes from the Greek "actis", which means "beam". Therefore, the tumor has another name - "solar keratoma". Most of the time it is multiple. The main localization - areas of the body most exposed to sunlight: bald areas of the scalp, forehead, back of the nose, cheeks, lower lip, auricles, skin of the forearms and the back surface of the hands.
The lesions may be irregular, round or oval in shape from 1 to 25 mm in diameter. As a rule, they are clearly separated from healthy skin and have an inflammatory red or pigmented brownish surface. Especially characteristic of them is hyperkeratosis (excessive keratinization), manifested by horny layers (yellowish, dirty brown or grayish-black in color) and roughness of the surface of the focus. In the affected area, sometimes there is a feeling of slight burning or itching.
In addition, there are other signs of damage from the sun's rays - the phenomena of skin elastosis (skin atrophy with proliferation of elastin fibers), areas of excessive pigmentation or, conversely, depigmented, as well as telangiectasia.
One of the frequent variants of actinic keratosis is also the skin horn described above, and actinic cheilitis - a skin lesion in the red border of the lips with inflammation, as well as on the line of contact of the lips, on the mucous membrane. As a rule, cheilitis occurs on the lower lip, as it is more prone to insolation than the upper lip. In the mechanism of its development, smoking is of no small importance.
Actinic keratoma is a precursor to squamous cell skin cancer.
Follicular keratoma
This type of neoplasm is extremely rare. It can occur at any age, but is most common after age 50. The tumor develops from the epithelium lining the funnel of the hair follicle and the hair canal. The neoplasm looks like a nodule of the correct spherical shape up to 1.5-2 cm in diameter, which slightly protrudes above the skin surface, has a grayish color or the color of the surrounding skin.
The surface of the keratoma is uneven: it is covered with small tubercles and contains a depression or a grayish scale in the center. Tumor foci are localized mainly on the scalp or on the forehead near the border of hair growth, on the cheeks, on the border upper lip, in the region of the nasolabial triangle, rarely - on the body and limbs.
How to get rid of keratomas
Given the external clinical similarity various kinds these tumors, one should keep in mind the complexity of their differential diagnosis and the possibility of transformation into skin cancer. Therefore, when they appear, it is necessary to monitor further development and visit a dermatologist at least once every 6 months.
Most often, keratomas grow very slowly and are not accompanied by any subjective sensations. In cases rapid growth, the appearance of a burning sensation, itching, causeless bleeding or numbness of the skin around the tumor, an immediate appeal to a specialist is necessary.
The main treatment of a keratoma is to remove it, followed by a histological examination of the tissue of the removed tumor. In some cases, in order to resolve the issue of the extent of the operation, a biopsy of the tumor site and its histological examination are performed.
In cases where there is complete confidence in the benign neoplasm, it is possible to remove it with liquid nitrogen or by means of electrodiathermy (electrocoagulation). However, in the case of the use of these methods of treatment, the keratoma tissue is completely destroyed, which does not allow for its subsequent study, and therefore, to be sure of the absence of malignant degeneration. In this regard, before removal, a histology of the tissue taken by knife or scarification biopsy is done.
In most cases, the keratoma is removed by a laser, less often by the traditional surgical method using a scalpel, after which, as after diathermocoagulation, a scar usually remains. The use of a laser allows you to gently remove the tumor by evaporation without damaging the surrounding tissues.
If, after removal, a red spot remains under the separated crust (also after cryodestruction), then an ointment is used for some time, which promotes faster cell regeneration and epithelialization of this area. However, the laser method does not allow further histological examination, so the latter has to be done before the operation.
Another way to get rid of the disease is to remove it by the radio wave method using the Surgitron apparatus. In this case, the operation is completely painless and usually does not require local anesthesia, there are practically no scars left after it, and the removed tumor can be subjected to histological analysis.
Treatment at home of a superficial small area keratoma is carried out using an ointment with an extract of celandine or lubricate this area with celandine juice long time. It is also possible to slow down the growth of the neoplasm as a result of the use of an ointment or balm containing an extract. bay leaf, oils walnut rubbing walnut balm, bandaging with aloe leaf or aloe juice.
However, all home methods based on traditional medicine can only be carried out after examination by a dermatologist and in accordance with his recommendations.
Neoplasms on the human body appear very unexpectedly. Some of them do not pose any harm to health, while others have a high chance of developing into malignant seals. Keratoma appears mainly in people over the age of 40 years. And the risk of its rebirth during this period is especially great!
What it is?
Keratoma is benign education on the human epidermis, formed during compaction, followed by keratinization of the cells of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. It is both vague and clearly defined dark growths along the contour. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 50 and 65 years. Gender doesn't matter at all. As unexpectedly as it appears, the keratoma may disappear. However, over time it will relapse. And again in the same place.
Causes
The main and most significant reason the appearance of keratoma on the body is age-related changes flowing in the epidermis. Localization of formations usually occurs in open areas exposed to aggressive ultraviolet rays.
In addition, provoke the appearance of the notorious plaques can:
- hereditary predisposition;
- violation normal operation immune system;
- dry skin;
- predisposition to the appearance of freckles, age spots, etc.;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- constant mechanical impact on the epidermis;
- constant skin contact and aggressive chemical compounds.
Kinds
Modern medicine knows several types of keratomas, differing from each other in their appearance, the nature of growth and the sensations of the patient himself. Each of them has its own approach to treatment, which allows to achieve optimal results in the shortest possible time.
The formation is a small nodule in a wide variation of colors: red, blue or black, without explicit forms and well-defined boundaries. The size of such a keratoma is from 1 to 10 mm.
The localization of plaques directly depends on the form of the neoplasm:
Sunny
Neoplasms appear mainly in areas of the skin that are not hidden under clothing: the face, back, limbs and are classified as precancerous diseases. Numerous scaly elements protrude slightly above the surface of the skin, and somewhat later degenerate into solid seals with erythematous tissues around. Remarkably, solar keratomas can suddenly disappear, and, after a certain period of time, appear in the same place. 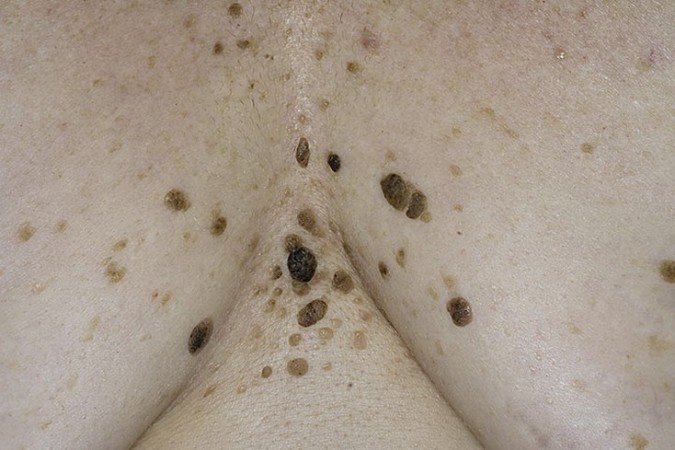
Follicular
Horny
First, a barely noticeable spot appears on the skin, from the keratinized elements of which a keratoma gradually forms. Distinctive features- these are its impressive dimensions, uneven surface and flaky areas. Sometimes such keratomas occur on their own, but there are also cases when they are the result of concomitant diseases(tuberculosis, lichen, etc.). Localization - head area and mucous membranes. Read more detailed information about in our article. 

seborrheic
Such a tumor grows quite slowly and reaches a maximum mark of 2-3 cm. It all starts with the appearance of a yellowish spot of similar size, the surface of which gradually thickens and becomes covered with scabs. Over time, the layers are compacted, and the color of the keratoma changes from yellow to brown and even black. Having reached a thickness of more than 1.5 cm, it is covered with deep cracks.
Damage to such a keratoma brings great discomfort and even causes bleeding. The area of occurrence is the face and neck. And, most importantly, seborrheic keratomas are often located in groups. ![]()
Symptoms
The formation of a keratoma of any kind begins with an unexpected appearance on the surface of the skin of a small spot of a grayish or beige color. It can be either completely flat or convex, protruding very slightly above the surface of the epidermis. Sometimes the stain is slightly flaky.
Gradually, the keratoma increases in size, and a dense crust forms at the site of the spot. It can spontaneously come off, but a new one will immediately form on the surface. Small bleeding is not excluded, as well as unpleasant and even pain upon contact of the neoplasm with other objects.
Treatment
When a keratoma appears, the patient must urgently contact a specialized specialist who will prescribe the optimal treatment. It is better to carry it out before the process of active growth and keratinization of the surface begins. Sometimes, in addition, the patient has to take tests to reliably determine whether education has developed into malignant form. This is done mainly in cases where the form of the disease is already too advanced.
The main therapy is to prevent the occurrence malignant formations. Most often, the patient is prescribed the antitumor antibiotic Bleomycin and cytostatics (Methotrexate, Cyclophosphamide, etc.). Similar active substances can be used to apply directly to the keratoma.
Effectively fights against small neoplasms (mainly seborrheic) and the drug "Solcoderm", which includes several groups of acids:
- lactate;
- ethandium;
- ethane;
- nitrogen.
Treatment should be carried out strictly under the supervision of the attending physician, possibly even under conditions day hospital. An incorrect approach to business can not only not give the desired result, but also lead to stimulation of keratoma growth.
Removal Methods
Removal of a keratoma is carried out in the presence of a clear aesthetic defect or in the absence of the effect of treatment for a long time. You can do this in the following ways:
- With a laser. This method considered one of the most modern and safe for the patient. It consists in the methodical impact on the neoplasm with a directed laser beam, which dries up the keratoma in about 15 minutes. In its place, a barely noticeable scar remains, which can be easily removed in a beauty salon.
- Standard surgery. The classic method used to excise the largest formations and adjacent tissues. The operation is carried out under local anesthesia, and in place of the keratoma, a standard surgical scar. It is used in advanced cases, when there is a high probability of degeneration of the formation into a malignant form.
- Electroexcision. Suitable for excision of small keratomas by point action of electric current. There are practically no traces left at the site of the operation, so you can even use an electric knife to remove formations on the face.
- Cryotherapy. It is mainly used to remove solar and seborrheic keratomas. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, freezing and subsequent death of the keratoma occurs in a matter of seconds. Painful sensations, as well as complications with this approach, are minimal.
- Radiosurgery. Non-contact excision allows you to save the patient from any kind of keratomas. The effect is achieved due to the effect of heat generated during the resistance of tissues to the penetration of high-frequency waves. After healing, even minimal scars or scars remain on the patient's skin.
Treatment at home
At the earliest stages of keratoma formation, traditional medicine methods may also be effective. However, they can be resorted to only if the approval of a professional physician is obtained.
And to help in the fight against "young" keratomas can:
- Aloe leaves. Each of them must be thoroughly washed and frozen for several days. At the end of the term, the leaves are cut and applied to the keratoma as a compress. The duration of treatment is 3 weeks.
- Potato. Raw potatoes need to be grated and applied to the formation. Keep the compress for about half an hour, and then thoroughly rinse the place of contact with warm water.
- Celandine. The juice of the plant is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and applied daily to the keratoma. Such actions not only reduce education, but also prevent the occurrence of relapse.
To slow down the growth of keratoma, it is necessary to include in the diet the maximum amount of foods containing vitamin P. These include legumes, green tea, buckwheat and much more.
Life prognosis and risks
With timely access to a doctor, the prognosis for the treatment of keratoma is quite favorable. After completing a medication course, or undergoing surgery, patients immediately return to their usual lives and no longer remember the disease.
In advanced cases, the risk of degeneration of keratoma is very high. And no one can predict how quickly oncology will progress.
Keratomas appear on the human body mainly after 40 years, when the body is especially vulnerable to negative conditions. environment. To minimize the likelihood of such a development of events, it is necessary to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, contact with harmful chemicals and take care of your skin. In addition, attention should be paid to the functioning of the immune system, malfunctioning, which entails a huge number of health problems.
Related Articles

Its appearance resembles a depressed raisin. It refers to benign neoplasms on the body and does not pose a health hazard until it develops into a malignant form or squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, treatment of keratoma should be mandatory and it should be started as soon as the first neoplasms are noticed.
How does a keratoma appear?
One of the main causes of keratomas that can appear on different areas body, consider excessive exposure to the skin of ultraviolet radiation. Getting on the skin Sun rays cause keratinization of the skin at the cellular level. Multiple or single neoplasms can appear on those parts of the body that most often fall under the sun: on the face, neck, back side hands.
- First, brown or yellow spots appear on the body, similar to freckles. They can be single or multiple, for example, senile (senile) keratomas.
- Gradually, the spots begin to darken, peel off and become hard.
- Then their size and appearance change: they increase to 1 - 2 cm.
- The top rough layer of the spot is covered with a crust, which can sometimes crack and bleed.
- The spot becomes convex and rises above the skin.
Ways to get rid
Treatment is carried out by various methods, including the practice of getting rid of them folk remedies. The most popular methods for gentle removal of neoplasms on the skin are the following:
- cryodestruction - removal with liquid nitrogen;
- laser removal;
- radiosurgery (radio knife);
- electrocoagulation (removal by current).
Radical removal methods are also practiced:
- surgical excision with a scalpel;
- chemical cauterization of the skin, which is often used when choosing treatment with folk remedies.
Let's dwell on more detailed description methods for the treatment of keratosis.
Cryodestruction
The most popular method today is cryodestruction, in other words, removal with liquid nitrogen. This method is considered affordable for many, unlike more expensive ones, such as removing a keratoma with a laser beam or current. The procedure itself is quick, but the rehabilitation process is very long and takes almost six months.
The essence of the procedure is as follows: very cold liquid nitrogen is applied to the keratosis, which burns out the neoplasm. severe pain at the same time, it is not felt, since nitrogen immediately after contact with the skin evaporates quickly. When liquid nitrogen gets on the skin, the patient feels a tolerable burning sensation and tingling. After that, the treated area of the skin becomes numb, swelling appears. Within a few days, the neoplasm disappears. A wound remains in its place, which heals over time.
When removed by this method, the probability of scarring of the skin is 70%. Therefore, the treatment of keratosis on the face is not recommended in this way. Although the removal of keratoma with liquid nitrogen is very popular, this method cannot be called effective.
Laser removal
Treatment of keratoma in this way is carried out quickly and painlessly. The essence of the procedure is as follows: laser ray is sent to the area of the skin where the keratoma is located and evaporates it by means of laser radiation. You can remove a keratoma with a laser on the face, on the body, on the scalp - there are no restrictions. There are no scars after the procedure, healing lasts no more than 2 weeks.
Radiosurgery
Removal of keratoma is also carried out with the help of radiosurgery. The bottom line is that the neoplasm is subjected to non-contact exposure to high-frequency radio waves using a special drug surgitron, which in the common people was called a radio knife. The operation to remove a keratoma in this way is very effective: the radioknife immediately cuts, disinfects and stops the blood. Anesthesia is given before the operation. There is no pain or swelling after the procedure.
Electrocoagulation
Treatment of keratoma can be carried out by the method of electrocoagulation - by exposing it to an electric current. The essence of the method is as follows: with a special device, the doctor acts on the keratoma with an electric current discharge. This method is more effective than liquid nitrogen treatment of keratosis, but it has its drawbacks. One of them is that in this way the keratoma can not be completely removed, and scars may remain in its place after removal.
Surgical excision
Highly old method, which is still used for the treatment of keratosis. The bottom line is that the neoplasm is cut off with a scalpel, after the operation, sutures are applied to the wound, which are removed after a few days. After surgical excision of a keratoma, scars remain on the body.
Chemical cauterization
This method is currently considered irrelevant and even, one might say, dangerous. It is more often practiced by lovers to use folk remedies at home. The bottom line is that chemical caustic substances are applied to the neoplasm: acids, alkalis and mineral salts. It is very dangerous to practice this method of getting rid of keratitis at home with folk remedies. This method can lead not only to the formation of scars at the site of removal, but also the development of a malignant tumor, and its transformation into squamous cell carcinoma.
Folk methods
It is impossible to completely get rid of keratomas with folk remedies. Most often, prepared preparations at home help soften the hard, keratinized top layer. So, at home, it is recommended to wipe keratomas with vegetable oils heated to a warm state.
Also, in case of injury, they practice wiping with a balm of walnut fruits or carry out treatment with celandine.
- To prepare a walnut balm in a ratio of 1 to 6, mix the crushed peel of an unripe fruit with a vegetable or vegetable heated to 45 - 50 degrees. castor oil. During the day, the balm is infused in a thermos, filtered and gently rubbed into the keratoma.
- Also, before complete removal of the keratoma, you can try to treat at home with a mixture prepared from crushed celandine leaves mixed with pork fat.
But once again we emphasize that the treatment of keratosis at home with the help of folk ways does not get rid of them, but is only a procedure that will help soften the top layer and prevent it from cracking.
Types of keratomas and methods for their removal
For the treatment of various keratomas practice different ways treatment.
| Type of keratoma | a brief description of | Methods of treatment |
| seborrheic keratosis | A yellow or brown raised spot on the skin, covered with a greasy crust on top; The crust may crack, fall off and bleed; It occurs in people over 50 years of age. |
laser removal; Cauterization with nitrogen; Lotions from prospiridone and fluorouracil ointment at home. |
| Keratoma senile | Multiple spots of grayish or whitish color, which are localized on the face, neck and back of the bones. It occurs after the age of 30 years. |
laser removal; Electrocoagulation; Surgical removal; Lotions with vegetable oil. |
| solar keratoma | Appears in people with fair skin with too strong and frequent exposure of the skin to sunlight; The formations are dense, covered with a gray crust on top. |
Nitrogen burning; laser destruction; The use of anticancer ointments. |
| Follicular keratosis | Small flat nodules of a gray tint that occur in the scalp. | Electrocoagulation; Scalpel cutting. |
| Horny keratoma | The height of the neoplasm is 5 - 7 mm; Dark color; It quickly develops into a cancerous tumor. |
Surgical removal; Radio wave removal; laser method. |
Keratosis is not dangerous to health: neoplasms do not always turn into skin cancer, but the treatment and removal of especially large ones and those that are often injured, for example, senile and horny, experts recommend starting as early as possible.
It is also necessary to remember that there are several types of keratomas, the removal of which should be carried out as early as possible: senile and seborrheic - they often turn into cancerous tumors. Their treatment at home is ineffective.
Keratomas - benign neoplasms that appear on human skin. Formations do not bring pain or harm. Removal of a keratoma is purely cosmetic. For this, medicine is used various methods: laser, radio wave, cryodestruction, liquid nitrogen removal. Each of them has pros and cons. It is worth studying in detail the nuances in order to choose the right option.
Removal of a keratoma is an aesthetic procedure that, with medical point vision is not necessary.
What is a keratoma?
Skin lesions that are brown or dark brown in color are called keratomas. Growth is characteristic of keratomas. Initially, the formations look like freckles or dark spots, over time they grow, reaching a size of 1-2 cm. The spots gradually become horny, peel off, the color approaches black. Neoplasms are single, but sometimes their number reaches several dozen. frequent place localization - arms, neck, back, less often appear on the lower extremities.
Dermatologists call the main reason for the formation of keratoma long stay in the sun. Ultraviolet rays create favorable conditions for keratinization of epithelial cells, contributing to the development of tumors.
The disease is asymptomatic, but there are cases when keratomas itch and hurt. The consequences are terrible - the growth of a tumor into a malignant one takes 7-15% of cases. Therefore, do not be careless about this disease. Some formations tend to peel off and fall off by themselves. But be sure to consult a doctor.
 It is worth thinking about removing a keratoma if it grows, bleeds, or is injured.
It is worth thinking about removing a keratoma if it grows, bleeds, or is injured. Do I need to remove a keratoma and why?
To remove the tumor or not is an individual decision for everyone. Some patients do not consider it necessary to remove solar keratosis, because it does not cause pain. But doctors recommend eliminating these formations. Removal is inevitable if additional factors are present:
- the tumor rises above the skin and is often injured;
- education is growing rapidly;
- the skin is often affected by ultraviolet rays;
- there were cracks and bleeding.
Neoplasms on the face bring special aesthetic discomfort, because they are very noticeable. The second place is occupied by formations that are amenable to constant friction. They are injured, an infection gets there, which threatens dangerous diseases. Keratomas that peel and crack gradually develop into malignant tumors. To prevent the problem from getting worse, it is worth removing the formation in time.
Removal Methods
Before choosing to remove a keratoma, you should consult a dermatologist. He will select an option based on the form, appearance and patient spot size. If there is a suspicion of a cancerous tumor, a histological examination is mandatory. In medicine, keratomas are removed using: laser, liquid nitrogen, electric current, acids and other methods. There are a number of contraindications in which the removal of neoplasms by any means is not recommended:
- diabetes;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- cardiovascular insufficiency;
- infectious diseases.
Laser removal
Removing a keratoma with a laser is a quick and painless method. The laser acts on a specific area without damaging the healthy epidermis. Laser removal of keratomas eliminates bleeding, because coagulation of the vessels occurs. The risk of relapse is low. Via laser method it is even possible to remove a keratoma on the face. The beam completely evaporates the tumor, leaving no scars and scars. In 1-2 weeks the skin is restored after the operation. During this time, visits to solariums and beaches are prohibited.
 Cryodestruction of a keratoma is quick and painless, but there is a risk of re-development of the neoplasm.
Cryodestruction of a keratoma is quick and painless, but there is a risk of re-development of the neoplasm. Removal with liquid nitrogen
Cryodestruction of keratoma or removal with liquid nitrogen is used for formations small size. When exposed low temperatures on education, it dies and falls away. An anesthetic is not used during the operation, so the person feels a slight burning sensation. After removal, the tumor is covered with a crust. If a bubble has formed, do not touch it. After a week, the crust will fall off, redness will become invisible. A small scar remains in place, which dissolves over time.
The disadvantage of this method is possible relapse. The depth of nitrogen exposure cannot be controlled, so not all tumor cells can be obtained using cryodestruction. Sometimes the depth is too great and a scar remains at the site of the removed formation.
Electrocoagulation
With the help of an electric current, the tumor tissue is cauterized. After electrocoagulation, a crust appears at the site of the tumor, and the skin heals under it. After 1-2 weeks, the peeling of the crust occurs. If there is a red spot left, do not worry - after a month there is not a trace left of the wound. The advantage of the method is minimal bleeding during the operation, because the current cauterizes the vessels. There are no scars or scars. However, people who have problems with the tolerance of electric current, suffer from hypertension, arrhythmia, this method is contraindicated.
 Surgically, it is appropriate to excise large keratomas.
Surgically, it is appropriate to excise large keratomas. Faced with various growths and neoplasms on the skin, people wonder, for example, when does a keratoma appear, what is it? Any neoplasm on the skin, even if it appeared a long time ago, but increases in size, hurts or itches, should cause concern in a person and serve as a reason to see a doctor.
Keratomas are formations on the skin that appear due to a sharp growth of the stratum corneum of the skin. In most cases, these neoplasms do not carry any danger and appear in people over 45 years of age. But like any other changes in the skin, under adverse factors can cause skin cancer.
Reasons for the appearance of neoplasms
Skin keratoma can appear for a number of reasons. As a rule, the root cause is rather difficult to establish. Also, the exact factors that can lead to the degeneration of a keratoma into a cancerous tumor have not yet been established.
Doctors have established the causes that can affect the appearance of keratomas on the human body:
Types of neoplasms
Keratomas on the face and body can be of several types. The differences between them lie in appearance, symptoms and causes.

Senile keratosis
Senile keratoma (senile keratosis). This type of neoplasm is common in people over 50 years of age. A feature of such formations is that they can be painful, and with little damage they can bleed.
Initially, spots appear on the face, head, or limbs. They are usually light or just brown, visually these areas of the skin resemble slight pigmentation. After a while, the spot begins to become brighter and darker. There is an increase in size, and the rise of the spot above the level of the skin.
The surface of the neoplasm is bumpy and loose to the touch. It shows education dark spots, veins and bumps. Usually the size of a senile keratoma does not exceed 2 cm in diameter. In some cases, the keratoma brightens.
Seborrheic keratoma. A distinctive feature of this neoplasm on the skin is its rather slow growth. As it grows and increases in volume, a growth with a sebaceous surface appears on the surface of the seborrheic keratoma. When injured, it is easily separated from the keratoma itself.

seborrheic keratoma
Seborrheic keratoma is dark brown or black in color. It is quite large in size from 1.5 cm. When damaged, it does not bleed much, but can bring very painful sensations. Quite often, seborrheic keratomas are present on the face and form in groups.
Horny keratoma. This neoplasm got its name from the visual resemblance to the horns of an animal. The formation of tissues of the horny keratoma comes from the layering of skin particles. At first it looks like a rise above the skin, then like a keratinized tubercle and, in the end, takes on the appearance of a small horn.
To the touch, the horny keratoma is very hard, it has scaly edges. In quite rare cases, the neoplasm does not look like a horn, but like a flat plaque above the skin. Horny keratoma may appear as a consequence serious illnesses including tuberculosis and lupus erythematosus.
Follicular keratoma. This neoplasm differs from the rest visually. Follicular keratoma is a pale pink spot of small diameter, which rises slightly on the surface of the skin, and is covered with small tubercles. In the center of the neoplasm is usually a depression, which is located on the same level with the skin.
![]()
solar keratoma
Solar keratoma. It can serve as one of the signs of approaching cancer. With solar keratoma, the skin of the face, hands and feet is covered with small scaly formations. Their scales are quite dense, but they are easily separated from the tumor itself.
Angiokeratoma is a formation on the skin in which its surface is covered with many small formations of brown, purple or black colors. This type of keratoma is quite common in newborns, in most cases they are mistaken for hemangiomas.
Diagnosis of keratoma
Before treatment, it is necessary to establish the presence of a neoplasm and its type. This will reduce the risk of misdiagnosis and, as a result, treatment. For example, in a child, some types of keratomas can be mistaken for hemangiomas or other neoplasms on the skin.
Examination of the skin and keratomas is carried out by a dermatologist and, if necessary, an oncologist. Before starting a full diagnosis, the doctor visually examines the formation. So he defines possible view education, its size, localization and approximate number.
Additional diagnostic tools can be:
- Inspection of a keratoma using a special device that increases the size of the formation - a dermatoscope.
- Comparative diagnostics is carried out in elderly people. Its purpose is to examine not only the keratoma itself, but also other neoplasms on the skin, comparison of keratoma and papillomas, warts, etc.

When a large number keratomas or their sharp increase in size, there is a risk of a malignant tumor of the skin. When this is possible, a histology of the keratoma is performed. To do this, a part of the formation is excised, and the cells are examined under a microscope. In an additional way diagnosis is an ultrasound of the formation and its biopsy.
Methods of treatment
The treatment of a tumor is to remove it.
Self-removal or treatment of neoplasms, especially on the face, can provoke the appearance of complications and even the risk of new keratomas.
At self-deletion there is a high risk of bleeding and a scar at the site of the neoplasm. With the worst outcome, squamous cell carcinoma may begin to form at the site of the neoplasm.
But it is not always necessary to remove a keratoma. Often it does not pose any danger to human health, and has only a negative cosmetic effect.
Removal of a keratoma is a method that helps to get rid of a neoplasm, and is the best prevention cancer and the appearance of new keratomas. The appearance of a new formation at the site of an old keratoma is possible in very rare cases.
Ways to get rid of keratoma:
- Cauterization with nitrogen. It is best to remove senile keratoma in this way. The doctor lubricates the surface of the formation with liquid nitrogen. In this case, anesthesia is not required, and the patient feels a burning sensation for only a short time. After a few days, all the tissues of the formation die, and the keratoma falls off. In its place, a pale pink spot may be present for a few more weeks, which will also disappear later.
- laser removal. This method is considered the most effective. In addition, laser therapy has practically no contraindications. With the help of a laser, both small and large keratomas can be removed. Another advantage of the laser is that it reduces the recurrence of neoplasms to zero.
- Removal with radio beams. This method is widely used in modern cosmetology. Its advantages are that radio waves act very gently and do not damage the tissues around the keratoma. In this way, small keratomas and formations on the face are removed, since radio waves do not leave scars and scars.
- Electricity. During electrocoagulation, a high-frequency current acts on the surface of the keratoma, which helps to instantly destroy its tissues. At proper care no scar or scar remains at the site of exposure. This method is suitable for removing large keratomas.
- Surgical method. Removal by excision is traditional method fight against keratomas. The operation is carried out under local anesthesia followed by a self-absorbable cosmetic suture. Surgical removal is performed if removal using other methods is not possible.
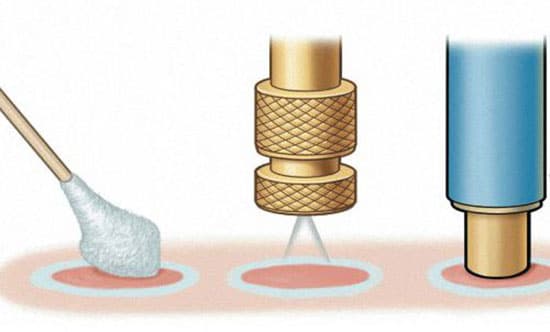
Treatment with traditional medicine
Such methods allow you to deal with neoplasms if their removal is impossible. Also ethnoscience helps to cope with formations on initial stage their appearance, and to carry out prevention against the further appearance of keratomas.
Regular lubrication with vegetable oil helps to soften the build-up tissues. Sea buckthorn, sunflower and fir oil. If the surface of the formation is injured, walnut paste will help heal it and avoid re-bleeding. Nuts are crushed to a powder state, and then mixed with baby cream or petroleum jelly. The resulting paste must be applied to the keratoma several times a day.
With large and painful keratomas, a bay leaf remedy will come to the rescue. The same tool is great for painful sensations, for example, when the growth is injured or rubs against clothing. To do this, bay leaves and juniper leaves are mixed in equal quantities. Then 12 parts are added to them butter. Everything is mixed up. To enhance the effect, you can add a few drops to the oil. essential oil fir.

At high risk oncology, it is urgent to remove keratomas, and before surgery, by any means, to fight its growth. This will help celandine. Substances of the plant literally burn through the tissues of the neoplasm, and do not allow the tumor to degenerate into cancer.
Prevention against the formation of new keratomas is common agrimony (burdock). Tea from it is recommended to be taken orally not only during treatment, but also after it. For this, the rhizomes of the plant are poured with boiling water, and infused for some time. Honey can be added to tea for flavor.
After removal of the keratoma and preventive treatment you need to take care of your skin for a while. You can wipe the place where the formation was formed daily with a solution of chamomile infusion or simple alcohol to avoid infection. In the diet, you need to increase the amount of foods with vitamin C.

